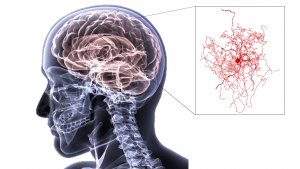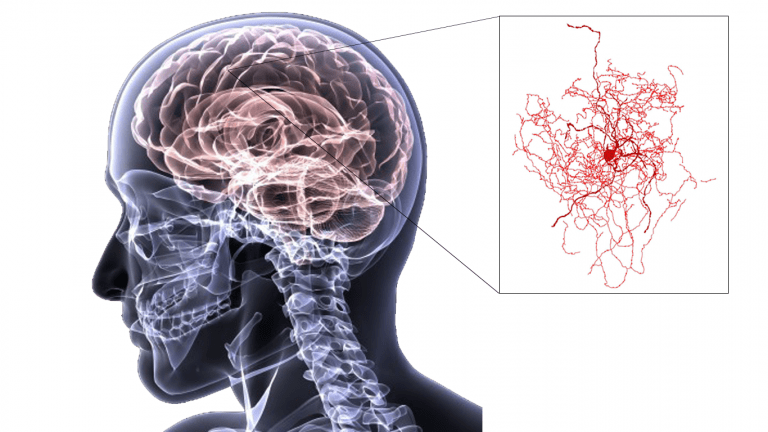
A reconstruction of a newly discovered type of human neuron. Image credit: U.S. Army graphic (human brain) and Boldog, et al. & Nature Neuroscience (rosehip neuron)
Table of Contents
Dubbed as “rosehip neuron“, a new brain neuron recently discovered is unique based on its morphology and the set of genes it activates. Neuroscientists recently uncovered this new type of neuron from postmortem human brain samples. They presumed that this rosehip neuron occurs in the brain of humans but not in rodents.
Rosehip neuron found in human brains
What makes human brain special? What sets it apart from other animal brains? Humans have this sort of consciousness and intelligence that make them different from other species. Apart from the complexity and the size of the human brain, its cellular components seem to be different from that of the other animals. Neuroscientists found rosehip neurons in human brain. These cells have not yet been observed in the brains of mice and other well-studied laboratory animals. Researchers reported this recent discovery in Nature Neuroscience.1 Nevertheless, they were fast to warn not to make haste assumptions. The rosehip neurons may not be unique to humans. More studies are on the way to confirm it.
What their findings implicate is the suitability of rodent brains as experimental models. Rodent brains lack such neurons. Thus, they may not be fit as laboratory models, especially when one tries to understand human neurologic diseases and how the brain works.
Current info on human rosehip neuron
Since rosehip neurons are a recent discovery, there is currently little information about them. What the neuroscientists know is they appear bushy. In fact, their bushy appearance accounts for their name “rosehip“. Rosehip originally refers to the accessory fruit of the rose plant. The rosehip neuron looks like the accessory fruit of the rose after petals are shed.
Researchers discovered the rosehip neurons from the top layer of the cortex of the brain from the postmortem brains of two men in their 50s. The rosehip neuron belongs to a group of inhibitory neurons. This means that it works by inhibiting other neuronal activity in the brain.
Researchers from the Allen Institute collaborated with the J. Craig Venter Institute. They found that the rosehip neurons seemed to have a different genetic signature. The rosehip neurons turned on a unique set of genes. They also formed synapses with pyramidal neurons. Pyramidal neurons are a different type of brain cells named after their shape.
Future research on rosehip neuron
Researchers have yet to fully recognize the purpose and importance of rosehip neurons in the human brain. In doing so, they may gain a significant insight regarding their role in neurologic function and diseases. They also aim to check the presence of rosehip neurons in other human brain parts as well as in the brains of other animals. Details on their recent work on rosehip neurons is published in Nature Neuroscience.2
— written by Maria Victoria Gonzaga based on the news release and materials from the Allen Institute website
Reference
1 Allen Institute. (27 Aug. 2018). Scientists identify a new kind of human brain cell. Retrieved from http://www.alleninstitute.org/what-we-do/brain-science/news-press/articles/scientists-identify-new-kind-human-brain-cell
2 Boldog, E. et al. (2018). Transcriptomic and morphophysiological evidence for a specialized human cortical GABAergic cell type. Nature Neuroscience. DOI: 10.1038/s41593-018-0205-2