Definition
noun, plural: hypothalami
A small region of the forebrain comprised of several small nuclei, located between the thalamus and the midbrain, and acts as the main control center for the autonomic nervous system as well as an endocrine gland secreting substances that control metabolism by exerting an influence on pituitary gland function
Supplement
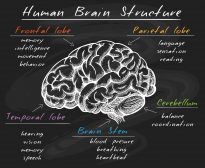
The brain is the organ that acts as the center of the nervous system of most animals, including humans. The three major regions of the human brain are the hindbrain (rhombencephalon), the midbrain (mesencephalonn), and the forebrain (prosencephalon). The forebrain, in turn, is comprised of two major portions: the diencephalon and the telencephalon. The hypothalamus is a small region in the diencephalon of the forebrain. It is located between the thalamus and the midbrain. The hypothalamus is comprised of several small nuclei. In humans, the hypothalamus has a size as that of an almond. The three major regions are anterior, tuberal, and posterior.
The anterior region of the hypothalamus is comprised of the preoptic, the medial, and the lateral areas. The preoptic area includes part of the preoptic nucleus. In the medial area, the hypothalamic nuclei included are (1) medial preoptic nucleus, (2) supraoptic nucleus, (3) paraventricular nucleus, (4) anterior hypothalamic nucleus, and (5) suprachiasmatic nucleus. In the lateral area, the hypothalamic nuclei included are the anterior part of the lateral nucleus, part of the supraoptic nucleus, and the lateral preoptic nucleus.
The tuberal region of the hypothalamus is comprised of the medial and the lateral areas. In the medial area, the hypothalamic nuclei are the dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus, the ventromedial nucleus, and the arcuate nucleus. In the lateral area, the tuberal part of the lateral nucleus and the lateral tuberal nuclei are located.
The posterior region of the hypothalamus is comprised of the medial and the lateral areas. The hypothalamic nuclei include part of the mammillary bodies and the posterior nucleus in the medial area and the posterior part of the lateral nucleus in the lateral area.
The hypothalamus acts as the main control center for the autonomic nervous system. It is also regarded as an endocrine gland. Certain neurohormones (referred to as releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones) are produced by the hypothalamic nuclei. Hypothalamic hormones act on the anterior pituitary gland, stimulating the latter to secrete hormones that influence other endocrine glands and organs. Other hormones are referred to as neurohypophysial hormones. These hormones are stored in and secreted from the axon terminals that extend to the neurohypophysis.
Some of the hormones secreted by the hypothalamus are as follows:
- thyrotropin-releasing hormone – produced by parvocellular neurosecretory cells of the paraventricular nucleus
- corticotropin-releasing hormone – produced by parvocellular neurosecretory cells of the paraventricular nucleus
- dopamine – produced by dopamine neurons of the arcuate nucleus
- growth hormone-releasing hormone – produced by the neuroendocrine neurons of the arcuate nucleus
- gonadotropin-releasing hormone – produced by the neuroendocrine cells of the preoptic area
- somatostatin – produced by the neuroendocrine cells of the periventricular nucleus
- oxytocin – produced by the magnocellular neurosecretory cells of the paraventricular nucleus and the supraoptic nucleus
- vasopressin – produced by the magnocellular and the parvocellular neurosecretory cells of the paraventricular nucleus, and by the magnocellular cells in supraoptic nucleus
It is also responsible for the secretion of ADH (anti-diuretic hormone) via its neurosecretory cells.
The hypothalamus plays a role in the following:
- thermoregulation
- osmoregulation
- regulation of blood sugar
- regulation of fat metabolism
- regulation of hunger and thirst
- regulation of certain aspects in parenting and attachment behavior
- controls sleeping patterns and circadian rhythms
- fatigue
See also:
Related term(s):
- Supraoptic nucleus of hypothalamus
Related form(s):