Definition
noun
(analytical chemistry)
A logarithmic measure of the amount of light absorbed (at particular wavelength) as the light passes through a sample or substance.
(microbiology)
The measure of the amount of light absorbed by a suspension of bacterial cells or a solution of an organic molecule with the use of a colorimeter or spectrophotometer.
Supplement
Absorbance measurements are often carried out in analytical chemistry, since the absorbance of a sample is proportional to the thickness of the sample and the concentration of the absorbing species in the sample.
Absorbance may be applied in plotting the growth of bacteria in suspension cultures. It may also be used in gauging the purity and concentration of molecules (e.g. proteins) in solution.
Although absorbance does not have true units, it is quite often reported in “Absorbance Units” or AU.
Word origin: L absorbére, equiv. to ab- + sorbére to suck in, swallow + –ance.
Related forms: absorbency (noun).
Synonym: optical density.
Compare: absorption.
Dictionary > Absorbance
You will also like...

Animal Growth Hormones
Hormones are produced in the endocrine glands of animals. The pituitary gland and hypothalamus are the most impor..

Early Mammals on Earth
The Earth's ecosphere was rapidly changing and throwing up a wide range of ecological niches that new adaptive organisms..

Consciousness and Behavior
Human consciousness and behavior are an interesting topic since they are determined and controlled by the brain. Conscio..
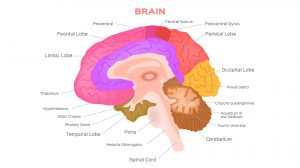
Human Neurology
Human Neurology deals essentially with the nervous system of humans. It also features the various theories put forward b..

Chromosomes X and Y and Sex Determination
This tutorial looks at sex determination via the sex chromosomes, X and Y. Read it to get more info on X and Y chromosom..

Ecosystem Succession
If the balance of nature is left untouched, landscapes can change dramatically over time. A previous ecosystem is supers..

