Analog
1. One of two organs or parts in different species of animals or plants which differ in structure or development but are similar in function.
2. A compound that resembles another in structure but is not necessarily an isomer (e.g., 5-fluorouracil is an analog of thymine); analogs are often used to block enzymatic reactions by combining with enzymes (e.g., isopropyl thiogalactoside vs. Lactose).
Synonym: analogue.
Origin: g. Analogos, proportionate
Dictionary > Analog
You will also like...
Amphibians & Early Reptiles
Obtaining air outside an aquatic environment required species to acquire suitable adaptations, and this was the case of ..

A Balanced Diet – Carbohydrates and Fat
Apart from vitamins, the human body also requires high energy sources such as carbohydrates and fats. If you want an ove..

Still Water Animals
Animals living in aquatic habitats have diversified and evolved through time. They eventually occupy ecological niches a..
Meiosis – The Genetics of Reproduction
Meiosis is a form of cell division that creates gametes. It is comprised of two divisions that in the end, the resulting..
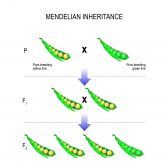
Inheritance and Probability
Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk, is most famous in this field for his study of the phenotype of pea plants, including ..

Biological Cell Introduction
It only takes one biological cell to create an organism. A single cell is able to keep itself functional through its 'mi..

