Analog
1. One of two organs or parts in different species of animals or plants which differ in structure or development but are similar in function.
2. A compound that resembles another in structure but is not necessarily an isomer (e.g., 5-fluorouracil is an analog of thymine); analogs are often used to block enzymatic reactions by combining with enzymes (e.g., isopropyl thiogalactoside vs. Lactose).
Synonym: analogue.
Origin: g. Analogos, proportionate
Dictionary > Analog
You will also like...

Biological Cell Introduction
It only takes one biological cell to create an organism. A single cell is able to keep itself functional through its 'mi..

Cell Respiration
Cell respiration is the process of creating ATP. It is "respiration" because it utilizes oxygen. Know the different stag..
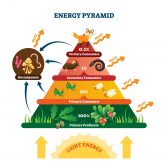
Freshwater Community Energy Relationships – Producers & Consumers
This tutorial looks at the relationship between organisms. It also explores how energy is passed on in the food chain an..

A Balanced Diet – Carbohydrates and Fat
Apart from vitamins, the human body also requires high energy sources such as carbohydrates and fats. If you want an ove..
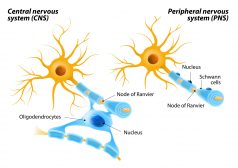
The Central Nervous System
Myelin sheath is essential for a faster conductivity of signals. Know more about this feature of some neurons in the Cen..

Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genes are expressed through the process of protein synthesis. This elaborate tutorial provides an in-depth review of the..

