Base analogue
(Science: biochemistry) a chemical which resembles a nucleotide base. They can substitute the purine and pyrimidine bases that normally appear in dna, despite minor differences in structure. May be used for inducing mutations, including point mutations.
For example: 5 bromouracil can replace thymine or 2 aminopurine replace adenine.
A foreign chemical that mimics the complimentary pairing of a genetic sequence, and usually proves to be a mutagen. This is because the base analogue harnesses the information on that particular
Dictionary > Base analogue
You will also like...
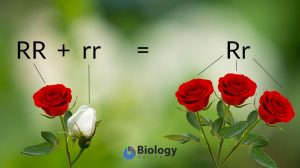
Dominance
This tutorial presents Gregor Mendel's law of dominance. Learn more about this form of inheritance and how it can be pre..

Control of Body Movement
Some of the body movements can be controlled at will, others cannot. The body has a motor program, which is the pattern ..

Selective Breeding
Gregor Mendel's studies into Monohybrid and Dihybrid crossing and Charles Darwin's study of evolution and natural select..

Developmental Biology
Developmental biology is a biological science that is primarily concerned with how a living thing grows and attains matu..

Arthropods
The arthropods were assumed to be the first taxon of species to possess jointed limbs and exoskeleton, exhibit more adva..

Homeostatic Mechanisms and Cellular Communication
Homeostasis is the relatively stable conditions of the internal environment that result from compensatory regulatory res..

