Bivalent antibody
antibody that causes a visible reaction with specific antigen as in agglutination, precipitation, and so on; so-called because according to the ”lattice theory aggregation occurs when the antibody molecule has two or more binding sites that can crosslink one antigen particle to another; probably a characteristic of the class of immunoglobulin.
Dictionary > Bivalent antibody
You will also like...

Roots
This study guide tackles plant roots in greater detail. It delves into the development of plant roots, the root structur..

Muscle
Muscle cells are specialized to generate force and movement. Learn about the different types of muscle tissues in this t..

Takahē (Porphyrio hochstetteri)
Meet the colorful takahē, an extremely rare flightless bird. Find out more about its unique features and why they matte..

Population Regulation in an Ecosystem
With regard to the population size of a species and what factors may affect them, two factors have been defined. They ar..

Ecosystem Succession
If the balance of nature is left untouched, landscapes can change dramatically over time. A previous ecosystem is supers..
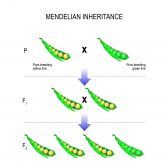
Inheritance and Probability
Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk, is most famous in this field for his study of the phenotype of pea plants, including ..

