Bivalent antibody
antibody that causes a visible reaction with specific antigen as in agglutination, precipitation, and so on; so-called because according to the ”lattice theory aggregation occurs when the antibody molecule has two or more binding sites that can crosslink one antigen particle to another; probably a characteristic of the class of immunoglobulin.
Dictionary > Bivalent antibody
You will also like...

Pollution in Freshwater Ecosystems
There are many environmental factors that arise due to the usage of water in one way or another and for every action tha..

Chemical Composition of the Body
The body is comprised of different elements with hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen as the major four. This tutorial..

New Zealand’s Unique Geographical History
Explore why New Zealand has such unique flora and fauna, and learn why long periods of geographical isolation. This less..

Fruits, Flowers, and Seeds
This tutorial deals with the structure and function of flowers, fruits, and seeds. Also included here are the types of f..

Takahē (Porphyrio hochstetteri)
Meet the colorful takahē, an extremely rare flightless bird. Find out more about its unique features and why they matte..
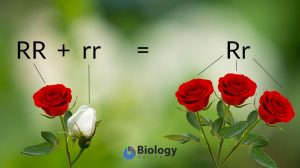
Dominance
This tutorial presents Gregor Mendel's law of dominance. Learn more about this form of inheritance and how it can be pre..

