![Botany n., [ˈbɑt.ə.ni/] botany definition and example](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/botany-definition-and-example-350x196.jpg)
Botany
n.,
[ˈbɑt.ə.ni/]
Definition: The scientific study of plant life.
Table of Contents
Botany is a highly diverse subject that encompasses several aspects of plants. When the question pops up, “what is a botanist?” it is commonly believed that a botanist is a person who studies plants and only identifies plants. But it’s more than that; it is not truly the answer to what does a botanist do.
The breadth of the subject prepares a botanist to not just identify but also work in different aspects of botanical research where the model organism is a plant (model plants). As you read this article, you will be enriched with small and big details about the subject.
Read on to learn how to define botany, and answer the common questions, like, what is a botany degree, what is medical botany, what is marine botany, how to define botanist, what is meant by botany science, what are vascular plants, … the different types of plant materials, the difference between flora (plant species) and fauna (animal species), conditions required for growing plants, etc.

Botany Definition
Botany is the domain of life sciences that focuses on plant life forms and their diversity; botany is the study of plants. Botany covered a variety of aspects of plant life like their morphology, anatomy, cell biology (branch dealing with plant cells), molecular biology, biochemistry, physiology (deals with phenomena related to plant growth), economic and ethnic aspects, taxonomy, environmental science, genetics, genomics, etc.
The breadth of the subject is so vast that it’s challenging to compile everything in a single article. Researchers working on plant biology (researchers who study plants are known as plant biologist or plant botanist) usually restrict themselves to a few selected aspect/s when they study a plant or research question of their interest.
The term botany finds its origin in the Greek word βοτάνη (botanē) which translates for “grass“, “pasture”, “fodder” or “herbs”. Botany is often referred to as plant science, botanical sciences, plant biology, or phytology (where ‘phyto’ stands for plants). This makes the scientist studying plants/Botany called botanists, plant biologists, plant scientists, or phytologists.
Biology Definition:
Botany is the branch of science that deals with plant life forms and their functions. It explores various aspects of plants like their growth, metabolism, constitution, ecological roles, etc. It is commonly also referred to as plant science or plant biology.
Etymology: Greek word βοτάνη (botanē) which means “grass“, “pasture”, “fodder” or “herbs”.
Synonyms: plant biology; phytology; plant science; botanical sciences
History of Botany
The history of Botany can be studied under 3 timeframes:
Early botany
The early history of Botany goes back to antiquity when human beings first started their explorations of the planet Earth. Botanical science is one of the world’s oldest natural sciences.
The curiosity of early humans has always revolved around the plethora of flora spread all around them. It is believed that the very first attempts of human beings to understand Botany as a subject were to know and differentiate between the diversity of plants and further characterize and describe their importance and uses. This was grossly related to “herbalism”.
Certain important plants to different religions and beliefs can commonly be identified near ancient religious and meditative places. Several ancient texts about plant classification and basic understanding of flora have been found in ancient civilizations of Southeast Asia like India, Iran, China, and Egypt. People of older cultures classified plants according to different rationales.


The modern history of Botany can again be studied under 2 timeframes:
Early modern botany
The early modern history of Botany (modern botany) goes back to Greek civilization where Theophrastus explained the science behind plant life in detail for the first time. For this reason, we often refer to him as the “Father of Botany”. His highly regarded work titled “Enquiry into Plants/Historia Plantarum” was one of the most stupendous contributions up till the late 15th century.
Another important contribution to the science of plant life was again from the Greek civilization by Pedanius Dioscorides who was a plant-based physician. He compiled a magnanimous amount of information about medicinally important plants (medicinal properties) in his literary work popularly known as “De materia medica”.
Padua botanical garden, one of the earliest botanical gardens was meticulously designed by Italians. In the mid-15th century, the world saw an upsurge in botanical curiosity leading to the establishment of several botanical gardens, parks, and arboretums. The world-renowned Kew Botanic Garden of the UK was designed in 1621.
Even the first microscopic examination of biological material was undertaken on a plant part “cork” by Robert Hooke, thus highlighting the early modern history of botany. Later compound microscopes brought more objectivity and clarity to plant structures.

Late modern botany
The late modern history of botany is closely associated with the colonialism by the Europeans all over the world. Since rich flora of the colonies could be easily accessed by the Europeans at that time, diversity of plant specimens were reaching Europe and western botany world in the early 18th century from different parts of the world. It was from here that a subject of Botany was formalized.
Carl Linnaeus officially contributed the first classification system in his work called “Species Plantarum” for plant life forms in order to bring more objectivity and rationale to the subject in 1753.
The binomial system of nomenclature took birth from this point where genus name precedes the plant species name (generic epithet, specific epithet). At this time, fungi and algae were included in the plant kingdom and studied under one (Cryptogamia) of the 24 groups described by Linnaeus in “Systema Sexuale”.
Several other naturists, physicians and people curious about plants and doing laboratory science made significant contributions in this time frame. Some of the important ones who should definitely be mentioned are Adanson, de Jussieu, Candolle, Bentham & Hooker, Charles Darwin, Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, Gregor Mendel (worked on pea plants pea plants), Stephen Hales, Joseph Priestley, Jan Ingenhousz etc.

Branches of Botany
A botanist studies many different aspects of the subject in the early career. These branches are highly diverse and can be categorized based on different parameters.
By Biology Subcategory
Branches of Botany as per the biological aspect are:
- Plant Anatomy
- Plant Morphology (deals with plant structure)
- Plant Genetics
- Plant Cell Biology/Cytology (scientific study of plant cells)
- Plant Ecology
- Plant Biochemistry
- Plant Biophysics
- Plant Taxonomy and Systematics, when asked what is systematics in botany, one can explain it as a subject that deals with the nomenclature, classification, description and correlation with evolutionary descent (relatives of near and distant past; deals with grouping of plants, grouped plants and natural history)
- Plant Biochemistry and Plant Physiology (deals with plant hormones, works around can use both living plant tissue and dead plant tissues)
- Plant Microbiology (how plants interact with microbes, types of microbes)
- Plant Genomics
- Plant Molecular Biology
- Paleobotany (the study of plant fossils)
- Ethnobotany, when asked what is ethno botany, one can explain it as a subject that deals with the ethnic knowledge of indigenous groups and cultures to utilize their plant wealth for various purposes
- Economic Botany
- Population genetics (deals with genetic inheritance in plant populations)
- Plant genetic engineering
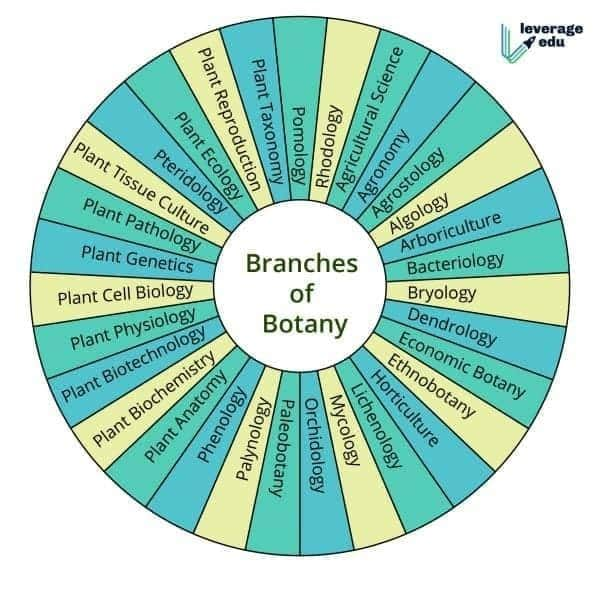
And there are even more specific branches.
By Type of Plant
The plant kingdom is majorly divided into bryophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms and angiosperms (flowering plants). Based to this, the branches of botany are:
- Bryology: It is the branch that deals with bryophytes (mosses).
- Pteridology: It is the branch that deals with pteridophytes (ferns).
- Anthology: It is branch that deals with flowering plants.
- Cryptogamic Botany: It is branch that deals with cryptogams (plants reproducing by spores).
- Phanerogamic Botany: It is branch that deals with phanerogams (plants reproducing by seeds).
Applied Plant Sciences
Further moving on, there are some branches that are categorized as per their applications in the practical world. Some of them to begin with are:
- Agronomy: It is the branch that deals with crops and soil science.
- Food science: It is the branch that deals with multiple aspects of food systems.
- Forestry: It is the branch that deals with forests and woodlands.
- Horticulture: It is the branch that deals with production of ornamental plants and of food crops.
- Natural resource management: It is the branch that deals with the conservations aspects of the different natural resources of Earth (soil, water, etc)
- Plant breeding: It is the branch that deals with the improvement of crop varieties that could be more useful for mankind.
- Plant pathology: It is the branch that deals with study of plant diseases and their respective pathogens.
- Pharmaceutical botany: It is the branch that deals with research of significant medicinal plants used in dietary supplements, phytotherapy, medicine and pharmaceutical technology. (This answers the question what is pharmaceutical botany)
Watch this vid about botany:
Importance of Botany
Botany or the study of flora has always been one of the most intriguing subjects for the human race. It has caught the sight and attention of generations of people time and again. The importance of learning basic botany is highlighted by the fact that every plant or tree around us has a very essential ecological function (plant functions) associated with it. If one recognizes that importance, the intrinsic way in which we act and function in this world would change. And that is the change world needs right now; a sustainable and responsible behavior of mankind in order to prevent extinction of the plant diversity on the planet.
Apart from this, theoretically there are many other important reasons for learning botany:
- Directly applicable in a number of practical world professions (example: Chefs use a number of different plants and flowers for the dishes that they prepare. Knowing the alternatives and substitutes (especially local alternatives of a vegetable) could come handy in developing new dishes)
- Important part of policy-making (Since the development of nations is in the hand of policy makers, it’s important that they are aware of the importance of flora of their country.)
- Advancement of Science (For developing new varieties and cultivars of plants that can survive the highly evolved pests and pathogens, its important that the botany knowledge/ scientific knowledge/ botanical knowledge is imparted to them).
Methods in Botany
There are many different methods to study botany. We’ll discuss a few of them here:
Morphological aspects
In the morphological aspect, the importance of studying the plant’s external morphology is highlighted. This method comes most handy when field biologists venture into wild spaces to study the floral diversity.
Being well-versed with the basic idea of herbs, shrubs and trees could be the first lifesaver. Learning how different types of vegetations like annuals, perennial and biennials appear in the world could also be hugely helpful.
Learning to differentiate bryophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms and angiosperms by their visually differentiating characteristic features is also something that’s essential for a botanist. Morphological method of plant identification is a time-tested method that helps one become a successful botanist.

Physiological aspects
Physiological method of understanding plants revolved around the biochemistry and physiology concepts. It focuses on the unmatchable photosynthesizing and oxygen-producing abilities (carbon dioxide-utilizing abilities) of green plants.
The first discoveries in the field of plant’s physiology were also related to these aspects. The advancement of science has facilitated scientists and researchers to take a leap in understanding how primary and secondary metabolites are produced by plants both of which are prized possessions for the human race.
Ecological aspects
Ecological method or aspect is one of the most crucial ones for botanists. It works at the conjunction of various other sciences and even stays relevant outside science. This is so because it is directly related to the economic, environmental and political aspects of life. There are a number of tools from physics, chemistry and statistics that play a direct significant role in the ecological studies.
Taxonomic aspects
Taxonomic aspect of botany is the oldest method that was studied in botany. Early naturalists and herbalists relied totally on the taxonomic keys for identifying medicinally important plants. Most of the historical works in botany involve majorly the taxonomic aspects. Even till date, the importance of taxonomic and systematic botany can’t be undermined in the major plant-based industries and plant pharmaceutical firms.
Botany Careers
There are a number of career options after pursuing botany. Some of the botany careers are:
- School and College professors
- Researchers and Scientists
- Landscaping artists (plants background or botanical background or botany background can be helpful in diversifying plant choice)
- Horticulturalists
- Plant consultants for big corps
- Forest officers and policy makers
- Environmentalists and NGOs working with tropical forests and their indigenous inhabitants
- Interdisciplinary research roles in companies (working both with plant and animal life)
Botany Major
Nowadays botany majors has been diversified in terms of the branch that one opts for like biotechnology, genetics, molecular biology, biochemistry, etc. Even introductory botany courses introduce young undergraduate learners to the basics of these specializations.
Sciences of Lichens, Fungi and Algae Aren’t Botany
Unlike other branches (e.g., bryology, pteridology, etc), lichenology, algology (or phycology) and mycology aren’t considered to be part of botany anymore. When the first classification systems of plant kingdom were introduced, both algae and fungi were studied by botanists. But as the science evolved and more sophisticates tools came into use, the older systems of classification became obsolete. Right now, we describe lichenology, mycology and phycology as follows:
- Lichenology is the branch that deals with lichens (symbiotic associations between fungi and algae where they are closely related).
- Mycology is the branch that deals with fungi.
- Phycology is the branch that deals with algae.

Answer the quiz below to check what you have learned so far about botany.
Further Reading
- Free Biology Tutorials – Plant Biology
- Plant sets off “SOS” for plant defense when it gets hurt
References
- Reed, Howard S. (1942). A Short History of the Plant Sciences. New York: Ronald Press.
- Martin, G. W. (1955). Are fungi plants?. Mycologia, 47(6), 779-792.
- Mukherjee, S. K., & Litz, R. E. (2009). Introduction: botany and importance. In The mango: Botany, production and uses (pp. 1-18). Wallingford UK: CABI.
- Purvis, M. J., Collier, D. C., & Walls, D. (1964). Laboratory techniques in botany. Laboratory techniques in botany.
- Strasburger, E. (1899). Handbook of practical botany.
- Harshberger, J. W. (1896). The purposes of ethno-botany. Botanical gazette, 21(3), 146-154.
- Simpson, B. B., & Ogorzaly, M. C. (1995). Economic botany: plants in our world (No. Ed. 2). McGraw-Hill Inc..
- Hall, M. (2011). Plants as persons: A philosophical botany. Suny Press.
- Bassi, D., & Monet, R. (2008). Botany and taxonomy. In The peach: botany, production and uses (pp. 1-36). Wallingford UK: CABI.
- Sachs, J. (1875). Text-book of botany: morphological and physiological. Clarendon Press.
©BiologyOnline.com. Content provided and moderated by Biology Online Editors.