Definition
noun, plural: bradyzoites
A slowly multiplying cell form in the life cycle of certain Apicomplexans, such as Toxoplasma gondii
Supplement
Apicomplexa is a phylum comprised of protozoans characterized by having a special organelle called an apical complex, and most of them are single-celled, parasitic, and spore-forming. They are intracellular parasites. Their life cycle is comprised of stages where each has a particular cellular variety. Nevertheless, not all members have all the various life stages.
Taking for instance the life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii (causative agent of toxoplasmosis), the various cell types in the life cycle of this species includes bradyzoites, tachyzoites, and oocysts. A bradyzoite is a sessile, slow-growing cell type. In latent toxoplasmosis, the bradyzoites form clusters within a cyst (pseudocyst) lodged in muscle and brain tissues of the host. The bradyzoites may give rise to either tachyzoites or gametocytes. Gametocytes, gamete-forming cells, may either be male or female. The male gametocyte differentiates into a microgamete that is flagellated and smaller. The female gametocyte becomes a macrogamete that is non-flagellated and larger in size than the male gametocyte. The male and the female gametocytes fuse forming a zygote inside the oocyst. The oocyst, therefore, contains the zygote. Under appropriate conditions, the zygote develops within the oocyst, which then becomes infective. Ingestion of the infective oocyst by the host could lead to toxoplasmosis. Within the host, the oocyst liberates bradyzoites in the stomach and intestine of the host and the parasite’s life cycle goes on again.
Word origin: brady– + Greek zōē (life)
See also:
Dictionary > Bradyzoite
You will also like...

Geological Periods
Geological periods is a study guide that cites the different geological periods on Earth's timeline. Each has a brief ov..

Cell Structure
A typical eukaryotic cell is comprised of cytoplasm with different organelles, such as nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, G..

Plant Metabolism
Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. Plant processes, such as photosynthesis, photop..

Gene Action – Operon Hypothesis
Learn how the way genes control and determine every aspect of the body. This lesson uses lac operon as an example. ..
..
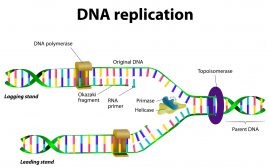
DNA Structure & DNA Replication
DNA is a double helix structure comprised of nucleotides. A nucleotide, in turn, is made up of phosphate molecule, deoxy..

Cell Biology
The cell is defined as the fundamental, functional unit of life. Some organisms are comprised of only one cell whereas o..

