Definition
noun
The part of the nervous system comprised of the brain, the brainstem, and the spinal cord
Supplement
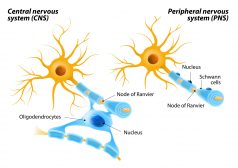
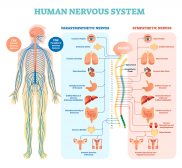
In vertebrates, the nervous system has two major divisions: (1) the central nervous system and (2) the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system consists of the brain, the brainstem, and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes the cranial nerves, the spinal nerves, the sympathetic nervous system, and the parasympathetic nervous system.
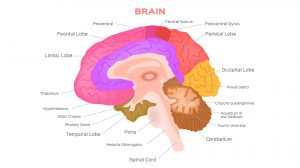
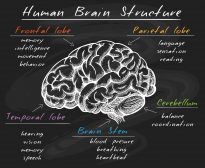
The central nervous system derived its name from its primary function, which is to serve as the center of processing information from all parts of the body. The brain is encased inside the skull whereas the spinal cord is contained inside the vertebral column. The spinal cord is continuous with the brain and lies caudally to it.
The central nervous system has two major types of tissues called white matter and gray matter. The white matter is comprised of axons and oligodendrocytes whereas the gray matter is made up of neurons and unmyelinated fibers. The white matter contains more glial cells than the gray matter.
In many invertebrates, the nervous system is composed of the segmental ganglia of the ventral nerve cord together with the fused ganglia or brain at the anterior end.
Abbreviation / Acronym:
- CNS
Also called:
- cerebrospinal axis
- systema nervosum centrale
See also:
- brain
- spinal cord
- neuron
- brainstem
- nervous system