Capping
1. Movement of cross linked cell surface material to the posterior region of a moving cell or to the perinuclear region.
2. The intracellular accumulation of intermediate filament protein in the pericentriolar region following microtubule disruption by colchicine.
3. The blocking of further addition of subunits by binding of a cap protein to the free end of a linear polymer such as actin.
See: cap binding protein.
Dictionary > Capping
You will also like...
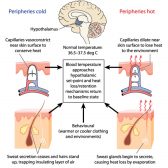
Temperature Regulation in Animals
This tutorial elucidates body temperature regulation. Know the details here to learn how the body sets the body temperat..

Consciousness and Behavior
Human consciousness and behavior are an interesting topic since they are determined and controlled by the brain. Conscio..

Seed Plants
Seed plants are vascular plants. They differ from the other vascular plants in producing seeds that germinate into a new..

Ecosystem Succession
If the balance of nature is left untouched, landscapes can change dramatically over time. A previous ecosystem is supers..

New Zealand’s Unique Flora
If New Zealand has lots of unique animals, it's also got a whole lot of unique plants. Find out more about some of them,..

Fruits, Flowers, and Seeds
This tutorial deals with the structure and function of flowers, fruits, and seeds. Also included here are the types of f..

