Cell Biology
Multifarious cell types that make up different tissues of a vascular plant
The cell is defined as the fundamental, functional unit of life. Some organisms are comprised of only one cell whereas others have many cells that are organized into tissues, organs, and systems. The scientific study of the cell is called cell biology. This field deals with the cell structure and function in detail. It covers topics such as DNA replication, protein synthesis, and cell defense.
Objectives
- To get to know the different organelles and cytoplasmic structures of the cell and be able to articulate their general composition and function
- To describe the various cellular processes, particularly cell respiration, photosynthesis, DNA replication, protein synthesis, and cell defense mechanisms
Key Points
- It only takes one biological cell to create an organism. A single cell is able to keep itself functional through its ‘miniature machines’ known as organelles.
- Cell respiration is the process of generating ATP by degrading sugar (glucose). ATP is essential to cell because it is the chief source of chemical energy that fuels many cellular activities.
- Autotrophs are capable of producing their own sugar (glucose) from inorganic sources and light. They do so through photosynthesis.
- DNA is a double helix structure comprised of nucleotides. A nucleotide, in turn, is made up of a phosphate molecule, a deoxyribose, and a nitrogenous base. The nucleotide sequence in the DNA codes for a particular protein.
- Proteins are synthesized inside the cell. Initially, mRNA transcript is generated. This is then brought to the ribosomes attached to the endoplasmic reticulum for translation. The newly synthesized protein undergoes post-translational modifications in the endoplasmic reticulum and in Golgi apparatus if the protein is to be transported outside the cell.
- Viruses are deemed as obligate parasites as they require a host to become “alive”.
- Organisms, such as animals and humans, have an immune system to combat antigens, especially those causing diseases. Plants may not have the same elaborate specialized cells to hunt down and kill antigens but they have their own strategies to defend themselves. They make use of hydrogen peroxide or chemicals, such as lignin, ethylene, galls, and tannins.
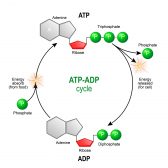
ATP & ADP – Biological Energy
ATP is the energy source that is typically used by an organism in its daily activities. The name is based on its structure as it consists of an adenosine molecule and three inorganic phosphates. Know more about ATP, especially how energy is released after its breaking down to ADP…
Cell Respiration
Cell respiration is the process of creating ATP. It is “respiration” because it utilizes oxygen. Know the different stages of cell respiration in this tutorial…
Photosynthesis – Photolysis and Carbon Fixation
Photosynthesis is the process that plants undertake to create organic materials from carbon dioxide and water, with the help of sunlight- all of which are investigated in this tutorial…
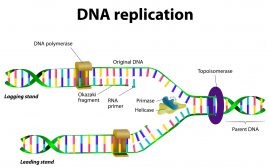
DNA Structure & DNA Replication
DNA is a double helix structure comprised of nucleotides. A nucleotide, in turn, is made up of phosphate molecule, deoxyribose, and a nitrogenous base. Know the fundamental structure of DNA and the process of DNA replication in this tutorial…
Protein Synthesis
Part of the genetic information is devoted to the synthesis of proteins. mRNA, a type of RNA, is produced as a transcript that carries the code for protein synthesis. Read this tutorial for further details…
Role of Golgi Apparatus & Endoplasmic Reticulum in Protein Synthesis
The endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus are the organelles involved in the translation step of protein synthesis and the ensuing post-translational steps. Read this tutorial for more info…
Protein Variety
The sequence of amino acids determines the type of protein. Protein is synthesized according to the sequence of nucleotides in the expressed DNA strand. For more info on the different types of proteins, read this tutorial…
Biological Viruses
Viruses possess both living and non-living characteristics. This unique feature distinguishes them from other organisms. They require other organisms to host themselves in order to survive and as such, they are regarded as obligate parasites. Learn more about viruses and cell assimilation in this tutorial…
Biological Cell Defense
Organisms employ different strategies to boost its defenses against antigens. Humans have an immune system to combat pathogens. Read this tutorial to learn the first and second lines of defense that the human body employs. ..
Passive and Active Types of Immunity
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell capable of producing a specific immune response to unique antigens. In this tutorial, learn about these lymphocytes and the mechanisms they employ to defend the body against the same antigens…
Plant Cell Defense
Plants protect themselves by releasing hydrogen peroxide to fight against fungal invasion. Another way is by secreting compounds, such as lignin, ethylene, galls, and tannins. Find out how these mechanisms protect the plants from pathogens…
Biological Cell Introduction
It only takes one biological cell to create an organism. A single cell is able to keep itself functional through its ‘miniature machines’ known as organelles. Read this tutorial to become familiar with the different cell structures and their functions…