Chromosomal crossover
Definition: homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange segments of their genetic material
Chromosomal Crossover Definition
noun
A process occurring during meiosis wherein homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange segments of their genetic material
More Info on Chromosomal Crossover
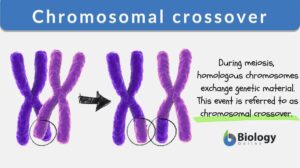
Chromosomal crossover occurs when homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material. This occurs at the stage when chromatids of homologous chromosomes pair up during synapsis, forming X-structure (chiasma). The chromatids break into segments (of matching regions), which are then exchanged with one another. The result is recombinant chromosomes. It particularly occurs in the pachytene stage of prophase I of the first meiotic division. Chromosomal crossover generally occurs when segments on homologous chromosomes break, and then, reconnect to the other of the matching chromosome. This was first demonstrated in 1931 by Harriet Creighton and Barbara McClintock.1 Chromosomal crossover between homologous chromosomes is important because it results in new combinations of genes that are different from either parent, contributing to genetic diversity.
Chromosomal crossover resulting in exchanges of unequal amounts of genetic material due to sequence mismatch may occur but not often. When this happens, it is termed as a non-homologous crossover or an unequal crossover. This results in an insertion or deletion mutation.
READ: Independent Assortment and Crossing Over
Watch this video to know what happens during crossing over
See also:
- Meiosis
- homologous chromosomes
- prophase I
Related term(s):
- Unequal crossing over
- Uneven crossing-over
Reference(s):
1 Creighton, H. and McClintock, B. (1931). “A Correlation of Cytological and Genetical Crossing-Over in Zea Mays”. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 17 (8): 492–7.
©BiologyOnline.com. Content provided and moderated by Biology Online Editors.