Cis trans test
(Science: molecular biology) The complementation test with two or more interacting genes placed in cis and in trans relationships to each other. A double mutant genome is used in the cis test made from the two single mutant genomes used in the trans test by recombination.
If the wild type phenotype is restored by both cis and trans arrangements it is concluded that the two mutations are in different genes and hence that the phenotype is determined by more than one gene. If the trans test is negative and the cis positive this means that the two mutations are in the same gene. If both tests are negative then at least one of the mutations must be dominant. Thus the double test provides a means of fine mapping of genes.
a lab test which is used to determine whether two mutations of different genes which affect the same phenotype are on the same functional unit (indicating a cis configuration of the mutated genes) or on different functional units (indicating a trans configuration of the mutated genes). (a functional unit can be a chromosome.)
The test is done by mating an individual that has one of the mutations to an individual that has the other one, and observing whether their offspring have the mutant phenotype. If the offspring do not have the mutant phenotype, then the genes are known to be trans, because the offspring have normal copies of each mutant gene on the different functional units which are able to genetically complement each other. If the offspring do have the mutant phenotype, then the genes are known to be cis, because the offspring will always inherit at least one of the mutant genes on the one functional unit, resulting in the mutant phenotype.
Dictionary > Cis trans test
You will also like...

Selective Breeding
Gregor Mendel's studies into Monohybrid and Dihybrid crossing and Charles Darwin's study of evolution and natural select..

Lotic Communities & Animals
A running water environment offers numerous microhabitats for many types of animals. Similar to plants, animals in lotic..

Developmental Biology
Developmental biology is a biological science that is primarily concerned with how a living thing grows and attains matu..

Control of Body Movement
Some of the body movements can be controlled at will, others cannot. The body has a motor program, which is the pattern ..

Mammalian Ancestors
Mammals are a diverse group of organisms, where most of them develop their offspring within the uterus of the mother. Ov..
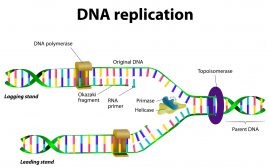
DNA Structure & DNA Replication
DNA is a double helix structure comprised of nucleotides. A nucleotide, in turn, is made up of phosphate molecule, deoxy..

