Condyloid joint
n., plural: condyloid joints
[ˈkɒndɪˌlɔɪd dʒɔɪnt]
Definition: a type of synovial joint, such as wrist joint, metacarpophalangeal joint, and metatarsophalangeal joint
Table of Contents
A joint is a point where two bones are attached and are capable of movement. The joints not only provide the movements of limbs but also provide stability (like the stability or hardness of the skull). The main function of joints is to hold the skeleton in a position and provide support in movements.
Joints can be categorized in two ways:
- Based on the function of the joint (the range of motion)
- Based on the structure of the joint (organization of the joint)
According to movements, there are three types of joints in the human body:
- Diarthroses (synovial joints) are freely movable
- Synarthroses (fibrous or fixed joints) are immovable
- Amphiarthrosis (cartilaginous joints) are slightly movable
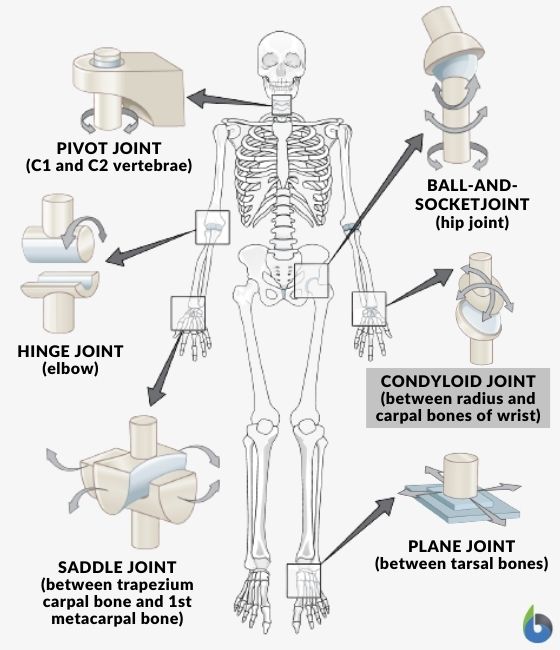
Synovial joints (diarthroses) is further divided into six types based on the type of joint movements:
- Hinge joint
- Pivot joint
- Condyloid joint
- Saddle joint
- Gliding joint
- Ball and socket joint
Condyloid Joint Definition
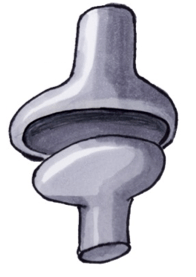
A condyloid joint is a type of synovial joint where the articular surface (meaning, the connection between the bones) of one bone has an ovoid convexity sitting within an ellipsoidal cavity of the other bone. (Yakut & Tuncer, 2020)
What is a condyloid joint?
The condyloid joint is a type of synovial joint. In one articular surface of the bone, there is an ovoid convexity in which it articulates with other bone having an ellipsoidal cavity. This joint allows rotation but no movement. For example, jaw and finger joints are condyloid joints.
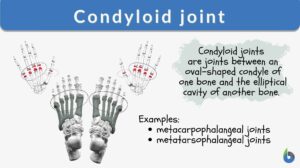
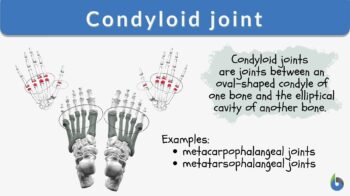
The condyloid joint is also named a condylar joint, bicondylar, or ellipsoid joint. The following figure shows a condyloid joint. In Figure 2, the oval shape end of one bone articulates with the oval shape hollow of another bone. (Manganaro, Dollinger, Nezwek, & Sadiq, 2019) For example, the metacarpophalangeal joint is a collection of condyloid joints that connects the metacarpus to the fingers. This is also an ellipsoid joint example.
In condyloid joints, the articular capsule is present among the two joined bones. Articular cartilage is the cover that protects the synovial joint. Certain adjacent ligaments to the joint provide support. They also help in preventing the injury by limiting the movement.
Hinge joints are different from condyloid joints. Hinge joints permit movement in only two planes and allow rotatory motion as well.
A condyloid joint is a type of synovial joint where the articular surface of one bone has an ovoid convexity sitting within an ellipsoidal cavity of the other bone. It allows movement in two planes (i.e., flexion or extension, abduction or adduction). Examples of condyloid joints are the wrist joint, the metacarpophalangeal joints, and the metatarsophalangeal joints.Etymology: Latin “condylus”, from Greek “kondulos”, meaning “knuckle”. Synonym: ellipsoidal joint; bicondylar; condylar joint. See also: synovial joints
Condyloid Joint Movements
Like saddle joints, condyloid joints permit movement with two degrees of freedom. Movement like abduction/adduction, flexion/extension (circumduction) is allowed at such joints. Axial rotation is allowed at the ball and socket joint but not at the condyloid joint. In other words, condyloid joints have non-axial movements. However, limited circumduction can be possible at such joints due to the oval shape of joints.
Although the fingers are small, limited circular motion is possible. The bottom joint of each finger is a condyloid joint. In the proper functioning of the hand, these joints have an important role. With the help of joint capsules, surrounding musculotendinous structures, and ligaments, flexibility and stability of fingers can be achieved. (Yakut & Tuncer, 2020)
Flexion/extension
Extension and flexion are the main movements at the condyloid joint. Almost 90° flexion, 10° extension in the index finger, and 30° extension in the little finger are possible. In the 3rd to 5th condyloid joint, flexion is accompanied by mild lateral rotation and in the 2nd condyloid joint it is accompanied by mild medial rotation.
Abduction/adduction
In the condyloid joint, about 25-30° full range of motion is possible around the axis. This small range of motion links to abduction. Due to collateral ligaments and the width and shape of the metacarpal head, the movement is restricted. Neither abduction nor adduction can be achieved in the condyloid joint during flexion. This happens due to the arrangement of collateral ligaments. Adduction and abduction are followed by the movements in the corresponding carpometacarpal joints.
Circumduction
In circumduction, the distal end of the limb moves circularly while the proximal end remains fixed. It includes the combination of adduction, abduction, flexion, and extension on a joint. This movement is possible at the multiaxial ball and socket joints, biaxial condyloid, and saddle joints.
Condyloid Joint Examples
Condyloid joints are present in the elbow, wrist joints, carpals of the wrist, and at the base of the index finger.
Examples are as follows:
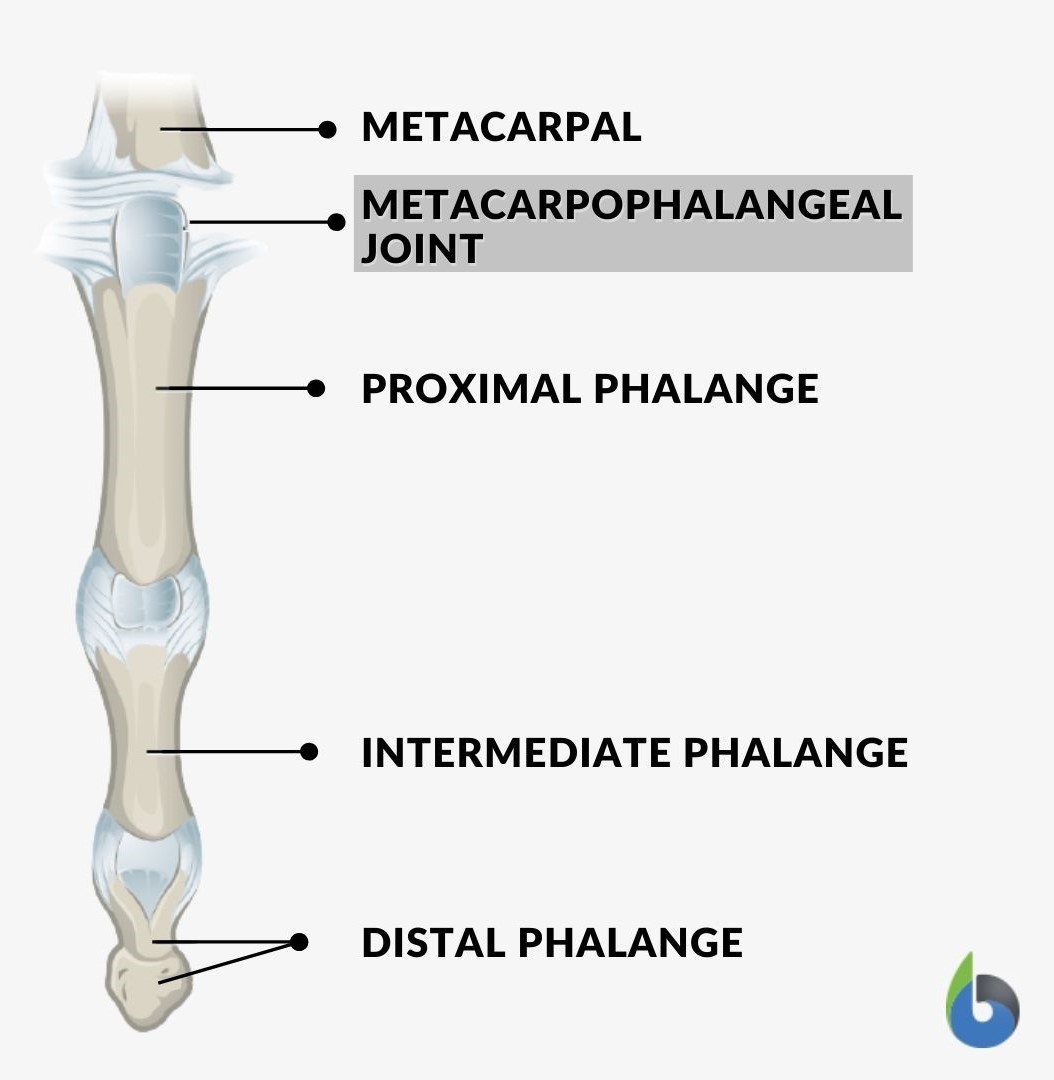
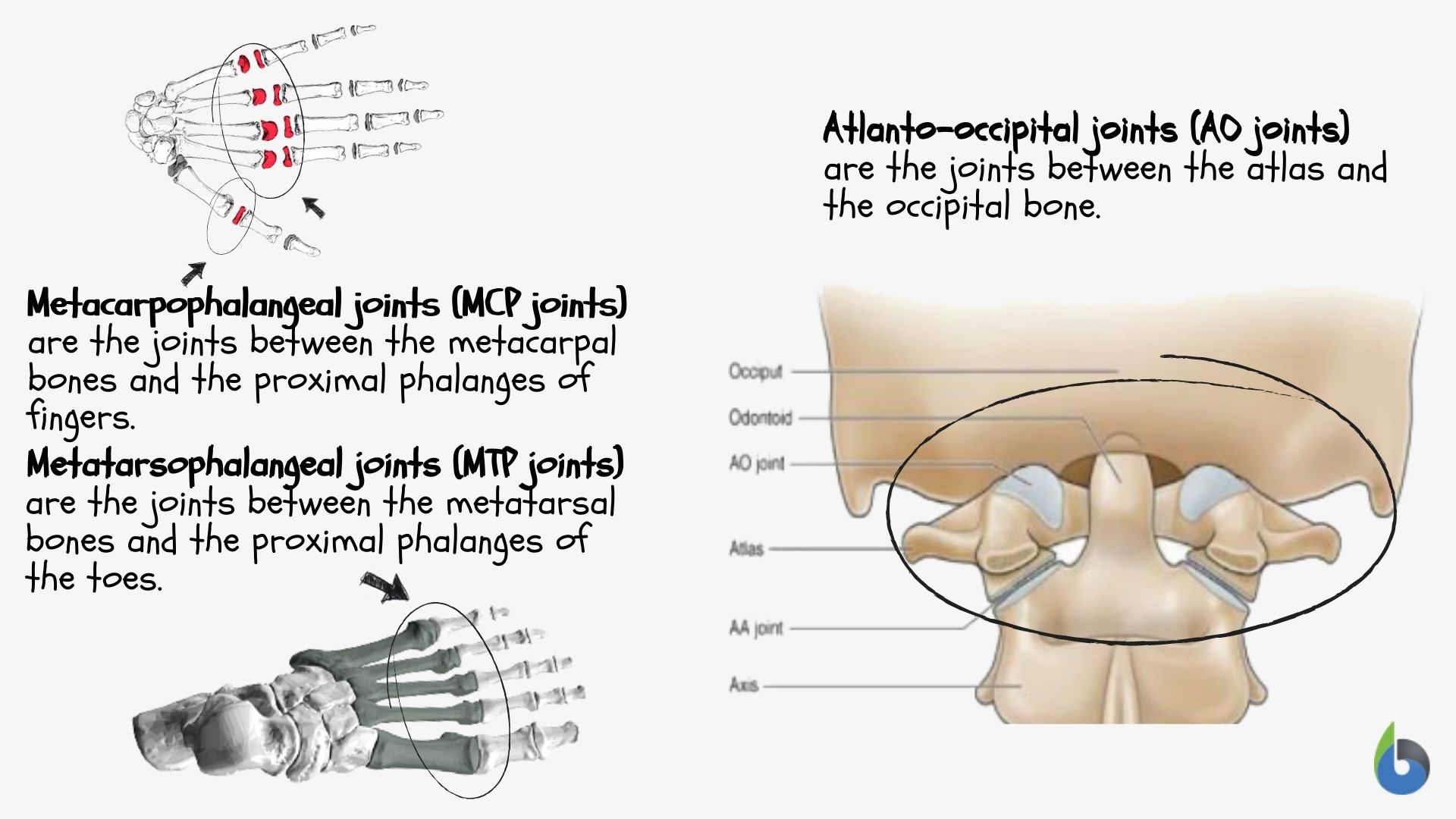
- Metacarpophalangeal joints (MCP)
The MCP joint is formed between the metacarpal bones and the proximal phalanges of the fingers. In this, the rounded head of the metacarpal articulates with the shallow cavity of proximal phalanges. Abduction, adduction, flexion, extension, and circumduction are allowed at this joint. - Metatarsophalangeal joints (MTP)
The MTP joint is formed in the foot, between the metatarsal bone and the proximal phalanges of toes. In this, the rounded or elliptical surface of metatarsal bone articulates with the shallow cavity of proximal phalanges. - Atlanto-occipital joints
This is another example of a condyloid joint. The articulation is between the atlas and occipital bone.
Try to answer the quiz below to check what you have learned so far about condyloid joints.
References
- Adrienne, L. (2015). Synovial joints: joint stability. Retrieved August 11, 2021, from https://pivotalphysio.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/A11.pngn
- Lumen. (2021). Types of Synovial Joints. Retrieved August 11, 2021, from https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wm-biology2/chapter/types-of-synovial-joints/
- Manganaro, D., Dollinger, B., Nezwek, T. A., & Sadiq, N. M. (2019). Anatomy, Bony Pelvis, and Lower Limb, Foot Joints.
- Yakut, Y., & Tuncer, A. (2020). Architecture of human joints and their movement. In Comparative Kinesiology of the Human Body (pp. 47–57). Elsevier.
©BiologyOnline.com. Content provided and moderated by Biology Online Editors.