Elephant
1. (Science: zoology) a mammal of the order Proboscidia, of which two living species, Elephas Indicus and E. Africanus, and several fossil species, are known. They have a proboscis or trunk, and two large ivory tusks proceeding from the extremity of the upper jaw, and curving upwards. The molar teeth are large and have transverse folds. Elephants are the largest land animals now existing.
2. Ivory; the tusk of the elephant.
(Science: botany) elephant apple, the tooth shell. See dentalium.
Origin: oe. Elefaunt, olifant, OF. Olifant, f. Elephant, L. Elephantus, elephas, -antis, fr. Gr,; of unknown origin; perh. Fr. Skr. Ibha, with the Semitic article al, el, prefixed, or fr. Semitic Aleph hindi indian bull; or cf. Goth. Ulbandus camel, as. Olfend.
Dictionary > Elephant
You will also like...

Plant Biology
Plantlife can be studied at a variety of levels, from the molecular, genetic and biochemical level through organelles, c..
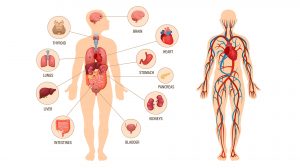
The Human Physiology
Physiology is the study of how living organisms function. Thus, human physiology deals specifically with the physiologic..

Biosecurity and Biocontrol
This lesson explores the impact of biosecurity threats, and why they need to be identified and managed. Examples to incl..
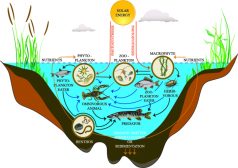
Freshwater Producers and Consumers
Freshwater ecosystem is comprised of four major constituents, namely elements and compounds, plants, consumers, and deco..
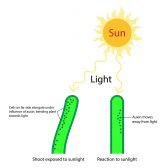
Plant Auxins – Phototropism & Geotropism
Plants produce hormones to regulate their growth. Auxins, for instance, influence plant growth. Know the role of auxin i..

Plant Cell Defense
Plants protect themselves by releasing hydrogen peroxide to fight against fungal invasion. Another way is by secreting c..

