Definition
noun
An aggregate of pigment molecules, each made up of cross-linked 5,6-dihydroxyindole (DHI) and 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid (DHICA) polymers, and is responsible for the black or brownish pigmentation of skin, feathers, hair, fur, eyes, scales, etc.
Supplement
Melanin is a term to refer to a group of pigments produced from the oxidation of tyrosine, followed by polymerization. It is produced by and stored in melanocytes or melanophores. The colours may vary and may be used as a basis for classifying melanin. There are three basic types of melanin: (1) eumelanin, (2) pheomelanin, and (3) neuromelanin.
Eumelanin is the most common and abundant type. It is composed of an aggregate of molecules that render brown or black in colour. Eumelanin polymer is made up of cross-linked 5,6-dihydroxyindole (DHI) and 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid (DHICA) polymers. There are two types of eumelanin, i.e. brown eumelanin and black eumelanin. Apart from the light-absorbing qualities that account for their respective colours, they also differ in the pattern of polymeric bonds. Eumelanin is produced through the process of melanogenesis, which includes a series of catalysed chemical reactions, starting from tyrosine, and with tyrosinase as the key enzyme.
In humans, it accounts for the pigmentation of the skin and hair. In particular, a small quantity of black eumelanin (in the absence of other pigments as well) results in gray hair. A small amount of brown eumelanin (in the absence of other pigments as well) results in blond hair. A defective tyrosinase production leads to the disruption of melanin production (including eumelanin) and therefore results in oculocutaneous albinism.
Word origin: eu– (true, well, good”) + Greek melas (“black, dark”)
See also:
Dictionary > Eumelanin
You will also like...
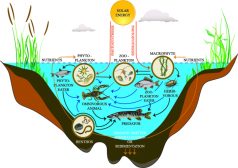
Freshwater Producers and Consumers
Freshwater ecosystem is comprised of four major constituents, namely elements and compounds, plants, consumers, and deco..
Genetics and Evolution
Humans are diploid creatures. This means that for every chromosome in the body, there is another one to match it. Howeve..

Lotic Communities & Algae
Lotic communities have conditions that are rather harsh for typical plants. Thus, the diversity of plant species in loti..

Vascular Plants: Ferns and Relatives
Ferns and their relatives are vascular plants, meaning they have xylem and phloem tissues. Because of the presence of va..

Cell Structure
A typical eukaryotic cell is comprised of cytoplasm with different organelles, such as nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, G..
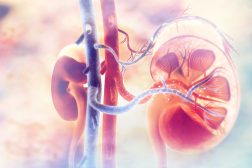
Homeostasis of Organism Water Regulation
Osmoregulation is the regulation of water concentrations in the bloodstream, effectively controlling the amount of water..

