Definition
noun
Antigen that enters the body of the organism from the outside, e.g. through inhalation, ingestion, or injection.
Supplement
Exogenous antigens include particles considered foreign within the organism. For example, allergens (such as pollen), proteins from transplanted tissues and organs, and parts of microorganisms (such as coat, capsule, cell wall, flagella, fimbria, or toxin of bacteria, viruses, etc.) can serve as antigens.
Word origin: French exogène : Greek exō-, exo– (outside) + French –gène, –gen (yielding, producing) + antigen.
Compare: endogenous antigen
See also: antigen
Dictionary > Exogenous antigen
You will also like...
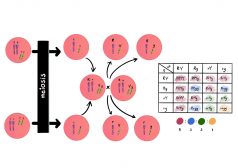
Independent Assortment and Crossing Over
This tutorial describes the independent assortment of chromosomes and crossing over as important events in meiosis. Read..

Mammalian Ancestors
Mammals are a diverse group of organisms, where most of them develop their offspring within the uterus of the mother. Ov..
Human Reproduction and Fertilization
For human species to obviate extinction, reproductive mature adults should be producing viable offspring in order to con..
Types and Causes of Brain Damage
This tutorial describes the different types and causes of brain damage. Find out how genetics, physical injury, lack of ..

Early Mammals on Earth
The Earth's ecosphere was rapidly changing and throwing up a wide range of ecological niches that new adaptive organisms..

Seed Plants
Seed plants are vascular plants. They differ from the other vascular plants in producing seeds that germinate into a new..

