Extraction coefficient
The percentage of a substance removed from the blood or plasma in a single passage through a tissue; e.g., the extraction coefficient for p-aminohippuric acid (PAH) in the kidney is the difference between arterial and renal venous plasma PAH concentrations, divided by the arterial plasma PAH concentration.
Dictionary > Extraction coefficient
You will also like...
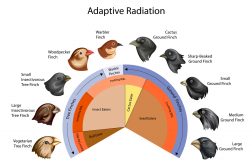
Adaptive Radiation
The diversification of several new species from a recent ancestral source, each adapted to utilize or occupy a vacant ad..

Plant Water Regulation
Plants need to regulate water in order to stay upright and structurally stable. Find out the different evolutionary adap..
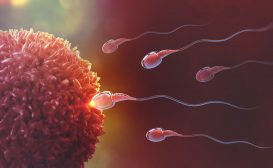
Human Reproduction and Fertilization
For human species to obviate extinction, reproductive mature adults should be producing viable offspring in order to con..

Still Freshwater & Plants
Plants in lentic habitats have features not found in terrestrial plants. They acquired these features as they adapt to t..

Fruits, Flowers, and Seeds
This tutorial deals with the structure and function of flowers, fruits, and seeds. Also included here are the types of f..

Hormone Production
Hormones are chemical messengers produced by specialized glands and they were produced by switching on the genes designe..

