Definition
noun, plural: gag reflexes
A reflex contraction characterized by retching or gagging when a foreign body comes in contact with the mucous membrane at the back of the throat, activating a sensory receptor that sends signals to the central nervous system, which ultimately activates effector cells to carry out appropriate responses that characterize the reflex
Supplement
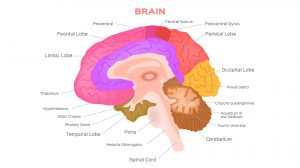
Reflex is an automatic instinctive unlearned reaction to a stimulus. The gag reflex is an example of it. Gag reflex is a reflex contraction that occurs when a foreign body comes in contact with the mucous membrane of the throat. The nerves take it as an external stimulus and then send a message to the central nervous system through the afferent nerve. The central nervous system responds by activating the effector cells via the efferent nerve. In particular, contact with the posterior pharyngeal wall leads to a retching or gagging. The soft palate elevates and the pharyngeal muscles contract bilaterally. This reflex is one of the natural preventive mechanisms that the body employs against objects in the mouth to reach other organs (e.g. respiratory tract) apart from those essential in swallowing. This reflex helps prevent choking.
In certain medical conditions such as damage to the glossopharyngeal nerve and the vagus nerve, the gag reflex is absent.
Synonym(s):
- faucial reflex
- laryngeal spasm
- pharyngeal reflex
See also: