Definition
noun
A metabolic pathway first delineated in depth by M. D. Hatch and C. R. Slack (in 1966).
In this pathway, the CO2 is first added to phosphoenolpyruvate by the enzyme, PEP carboxylase, producing the four-carbon compound in mesophyll cells that is later transported to bundle sheath cells to liberate the CO2 for use in the Calvin cycle.
Supplement
Instead of the direct carbon fixation in the Calvin cycle like in C3 carbon fixation, the C4 pathway involves steps that first converts pyruvate to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to bind with the CO2 forming a four-carbon compound (hence the name C4). As a result, the photorespiration pathway is bypassed, and the wasteful loss of CO2 common in C3 carbon fixation pathway is minimized.
Plants that first go through the C4 pathway are better adapted than plants that solely go through the C3 pathway under conditions of drought, high temperatures and low nitrogen or CO2 concentrations.
Word origin: from M.D. Hatch and C.R. Slack who first described it.
Synonym: Hatch slack kortshak pathway, C4 carbon fixation pathway.
Compare: C3 carbon fixation pathway, Crassulacean acid metabolism.
See also: C4 plant.
Dictionary > Hatch-Slack pathway
You will also like...
Homeostasis of Organism Water Regulation
Osmoregulation is the regulation of water concentrations in the bloodstream, effectively controlling the amount of water..

Mammalian Ancestors
Mammals are a diverse group of organisms, where most of them develop their offspring within the uterus of the mother. Ov..
Meiosis – The Genetics of Reproduction
Meiosis is a form of cell division that creates gametes. It is comprised of two divisions that in the end, the resulting..

Population Regulation in an Ecosystem
With regard to the population size of a species and what factors may affect them, two factors have been defined. They ar..

Abiotic Factors – Water Conditions
A still body of water may be disturbed by a variety of factors. One of them is wind. In fact, it is considered as the pr..
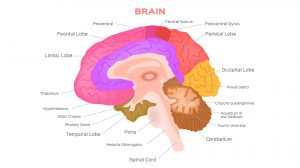
Human Neurology
Human Neurology deals essentially with the nervous system of humans. It also features the various theories put forward b..

