Definition
noun
A metabolic pathway first delineated in depth by M. D. Hatch and C. R. Slack (in 1966).
In this pathway, the CO2 is first added to phosphoenolpyruvate by the enzyme, PEP carboxylase, producing the four-carbon compound in mesophyll cells that is later transported to bundle sheath cells to liberate the CO2 for use in the Calvin cycle.
Supplement
Instead of the direct carbon fixation in the Calvin cycle like in C3 carbon fixation, the C4 pathway involves steps that first converts pyruvate to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to bind with the CO2 forming a four-carbon compound (hence the name C4). As a result, the photorespiration pathway is bypassed, and the wasteful loss of CO2 common in C3 carbon fixation pathway is minimized.
Plants that first go through the C4 pathway are better adapted than plants that solely go through the C3 pathway under conditions of drought, high temperatures and low nitrogen or CO2 concentrations.
Word origin: from M.D. Hatch and C.R. Slack who first described it.
Synonym: Hatch slack kortshak pathway, C4 carbon fixation pathway.
Compare: C3 carbon fixation pathway, Crassulacean acid metabolism.
See also: C4 plant.
Dictionary > Hatch-Slack pathway
You will also like...

Mendel’s Law & Mendelian Genetics
One of Mendel’s law of inheritance is the “law of dominance”. Read this tutorial to know more about this form of i..

Principles of Hormonal Control Systems
Hormones are essential in the regulation of the activity of the various biological systems of the human body. The ineffi..

Chromosomes X and Y and Sex Determination
This tutorial looks at sex determination via the sex chromosomes, X and Y. Read it to get more info on X and Y chromosom..
Plant Meristems and Growth
In plants, growth occurs in meristems, which are the site of repeated cell division of unspecialized cells. These cells ..
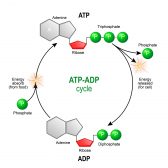
ATP & ADP – Biological Energy
ATP is the energy source that is typically used by an organism in its daily activities. The name is based on its structu..
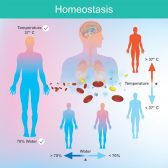
Physiological Homeostasis
Homeostasis is essential to maintain conditions within the tolerable limits. Otherwise, the body will fail to function p..

