Hexapoda
(Science: zoology) The true, or six-legged, insects; insects other than myriapods and arachnids.
The hexapoda have the head, thorax, and abdomen differentiated, and are mostly winged. They have three pairs of mouth organs, viz, mandibles, maxillae, and the second maxillae or labial palpi; three pairs of thoracic legs; and abdominal legs, which are present only in some of the lowest forms, and in the larval state of some of the higher ones. Many (the Metabola) undergo a complete metamorphosis, having larvae (known as maggots, grubs, caterpillars) very unlike the adult, and pass through a quiescent pupa state in which no food is taken; others (the Hemimetabola) have larvae much like the adult, expert in lacking wings, and an active pupa, in which rudimentary wings appear. See insecta. The hexapoda are divided into several orders.
Origin: NL, fr. Gr. Six – -poda.
Dictionary > Hexapoda
You will also like...

Vascular Plants: Ferns and Relatives
Ferns and their relatives are vascular plants, meaning they have xylem and phloem tissues. Because of the presence of va..

Bryophytes
Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) are a plant group characterized by lacking vascular tissues. They include the mosses, th..
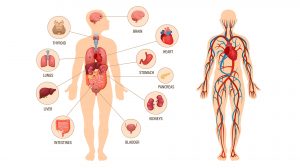
The Human Physiology
Physiology is the study of how living organisms function. Thus, human physiology deals specifically with the physiologic..

Photosynthesis – Photolysis and Carbon Fixation
Photosynthesis is the process that plants undertake to create organic materials from carbon dioxide and water, with the ..

Meiosis and Alternation of Generations
Plants are characterized by having alternation of generations in their life cycles. This tutorial is a review of plant m..

Genetic Mutations
This tutorial looks at the mutation at the gene level and the harm it may bring. Learn about single nucleotide polymorph..

