Hopanoid
(Science: cell biology) hopanoid is a chemical component in the cytoplasmic membranes of many bacteria.
hopanoid is a pentacyclic saturated derivative of mevalonic acid (mevalonic acid is a key intermediate in cholesterol biosynthesis) and is assumed to be functioning in a similar way to sterols, which serve to stabilise the structure of eukaryotic membranes.
while sterols can make up 5-25 percent of the total lipids of eukaryotic membranes, they are absent from most of the prokaryotic membranes.
Dictionary > Hopanoid
You will also like...

Fish
The sea was teeming with life. Eventually, through reproduction and continued variation, fish came about. There are over..

Hormone Production
Hormones are chemical messengers produced by specialized glands and they were produced by switching on the genes designe..
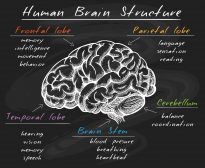
The Conscious & Unconscious Nervous System
This tutorial elaborates on how the nervous system works, particularly at the tissue level of the brain. There are three..

Community Patterns
Learn about community patterns and the ecological factors influencing these patterns. Revisit some of the ecosystems you..

Bryophytes
Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) are a plant group characterized by lacking vascular tissues. They include the mosses, th..

Ecological Research: Measuring & Analysis
This lesson is about the methods used for ecological research, such as quadrat and transect sampling, canopy fogging, an..

