Hopanoid
(Science: cell biology) hopanoid is a chemical component in the cytoplasmic membranes of many bacteria.
hopanoid is a pentacyclic saturated derivative of mevalonic acid (mevalonic acid is a key intermediate in cholesterol biosynthesis) and is assumed to be functioning in a similar way to sterols, which serve to stabilise the structure of eukaryotic membranes.
while sterols can make up 5-25 percent of the total lipids of eukaryotic membranes, they are absent from most of the prokaryotic membranes.
Dictionary > Hopanoid
You will also like...

The Gene Pool and Population Genetics
According to Charles Darwin's theory of natural selection, preferable genes are favored by nature in the gene pool, and ..

Plant Water Regulation
Plants need to regulate water in order to stay upright and structurally stable. Find out the different evolutionary adap..

Population Regulation in an Ecosystem
With regard to the population size of a species and what factors may affect them, two factors have been defined. They ar..

Plant Tissues
Plant organs are comprised of tissues working together for a common function. The different types of plant tissues are m..
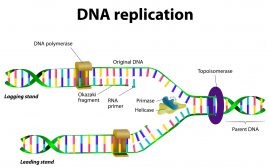
DNA Structure & DNA Replication
DNA is a double helix structure comprised of nucleotides. A nucleotide, in turn, is made up of phosphate molecule, deoxy..

Geological Periods
Geological periods is a study guide that cites the different geological periods on Earth's timeline. Each has a brief ov..

