Hormone Production

Negative feedback in the pituitary thyroid axis
Table of Contents
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.
Hormones are chemical messengers produced by glands in the endocrine system. Endocrine tissues secrete products that are carried to their target cells by the bloodstream or other tissue fluids. Hormones activate their target cells by binding to receptors in the target cell membrane. Human hormones are in three general categories: steroids, amino acid derivatives, and peptide hormones. Cortisone and estrogen are steroid hormones, epinephrine and thyroxine are amino acid derivatives and insulin and growth hormone are polypeptides.
Hypothalamus and the Pituitary Gland
Many hormones are regulated through the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus is a small region at the base of the brain and the pituitary hangs just below it. See the location of the hypothalamus and pituitary in the image above. The hypothalamus secretes releasing hormones that instruct the anterior pituitary gland to secrete certain hormones. One of the hormones regulated by this hypothalamus-pituitary axis is thyroxine, one of the thyroid hormones. Interactions between the thyroid, pituitary, and hypothalamus are illustrated in the image at the top of this page. The hypothalamus produces a thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which activates the secretion of the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the anterior pituitary. The TSH stimulates the release of thyroid hormones from the thyroid gland. The thyroid hormones in turn feed back to suppress both pituitary and hypothalamus hormone production. Both the hypothalamus and the thyroid also produce hormones of their own, e.g. growth hormone from the anterior pituitary and the antidiuretic hormone from the hypothalamus.
Note: The anterior and posterior pituitary are found together, but originate as separate structures. The posterior pituitary is part of the hypothalamus and stores some hypothalamic hormones. The anterior pituitary is derived from the roof of the mouth but migrates to the brain during early development.
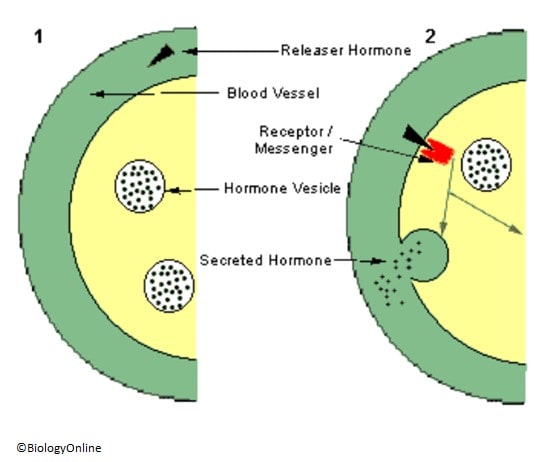
- In Figure 1 above, the releasing hormone from the hypothalamus finds its target tissue in the anterior pituitary. It binds to the receptor where a chemical messenger instructs the cell to release the pituitary hormone.
- The secreted pituitary hormone will instruct the target tissue to release its product. Endocrine glands regulated by the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary in this way include the adrenal cortex, the thyroid, and the testes and ovaries.
Hormone Use
Some of the uses to which hormones are put in humans are the following:
Insulin and glucagon are peptide hormones produced by islet cells in the pancreas and regulate blood sugar concentration. Insulin lowers the blood sugar by stimulating the uptake of sugar into various cells, while glucagon raises blood sugar by stimulating the release of glucose from glycogen stored in the liver.
Thyroid hormones are amino acid derivatives produced by the thyroid gland and help to regulate metabolism.
Estrogen, progesterone and testosterone are steroid hormones produced by the ovaries and testes. They regulate male and female sex characteristics, egg and sperm production, and pregnancy
Cortisone is a corticosteroid hormone produced by the adrenal cortex and helps to mediate stress responses.
Epinephrine (adrenalin) is an amino acid derivative produced by the adrenal medulla and mediates the “fight or flight” response to dangerous situations.
Growth hormone is a peptide hormone produced by the anterior pituitary. It stimulates cell growth and reproduction and also increases metabolism.
Prolactin is a peptide hormone made by the anterior pituitary and stimulates milk production during breast-feeding
ADH, the antidiuretic hormone, is a peptide hormone produced by the hypothalamus and regulates the amount of water reabsorbed by the kidneys.
The next tutorial investigates the use of these hormones in animals with successive pages studying plant hormones.
You will also like...

Population Regulation in an Ecosystem
With regard to the population size of a species and what factors may affect them, two factors have been defined. They ar..

A Balanced Vitamin Diet – Vitamins A – K
A balanced diet is essential to a healthy organism. Insufficiency or too much of a particular element or compound, such ..

A Balanced Diet – Carbohydrates and Fat
Apart from vitamins, the human body also requires high energy sources such as carbohydrates and fats. If you want an ove..

Running Water Freshwater Communities
This tutorial introduces flowing water communities, which bring new and dithering factors into the equation for possible..
Primitive Animals
Life, as we know it today, is presumed to have started in the sea and many of them were likely eukaryotic animal-like or..

Homeostatic Mechanisms and Cellular Communication
Homeostasis is the relatively stable conditions of the internal environment that result from compensatory regulatory res..
