Horse
1. To provide with a horse, or with horses; to mount on, or as on, a horse. Being better horsed, outrode me.
2. To sit astride of; to bestride.
3. To cover, as a mare; said of the male.
4. To take or carry on the back; as, the keeper, horsing a deer.
5. To place on the back of another, or on a wooden horse, etc, to be flogged; to subject to such punishment.
Origin: as. Horsion.
1. (Science: zoology) a hoofed quadruped of the genus Equus; especially, the domestic horse (E. Caballus), which was domesticated in egypt and asia at a very early period. It has six broad molars, on each side of each jaw, with six incisors, and two canine teeth, both above and below. The mares usually have the canine teeth rudimentary or wanting. The horse differs from the true asses, in having a long, flowing mane, and the tail bushy to the base. Unlike the asses it has callosities, or chestnuts, on all its legs. The horse excels in strength, speed, docility, courage, and nobleness of character, and is used for drawing, carrying, bearing a rider, and like purposes.
many varieties, differing in form, size, colour, gait, speed, etc, are known, but all are believed to have been derived from the same original species. It is supposed to have been a native of the plains of Central asia, but the wild species from which it was derived is not certainly known. The feral horses of America are domestic horses that have run wild; and it is probably true that most of those of asia have a similar origin. Some of the true wild Asiatic horses do, however, approach the domestic horse in several characteristics. Several species of fossil (equus) are known from the later tertiary formations of Europe and America. The fossil species of other genera of the family equidae are also often called horses, in general sense.
2. The male of the genus horse, in distinction from the female or male; usually, a castrated male.
3. Mounted soldiery; cavalry; used without the plural termination; as, a regiment of horse; distinguished from foot. The armies were appointed, consisting of twenty-five thousand horse and foot. (Bacon)
4. A frame with legs, used to support something; as, a clotheshorse, a sawhorse, etc.
5. A frame of timber, shaped like a horse, on which soldiers were made to ride for punishment.
6. Anything, actual or figurative, on which one rides as on a horse; a hobby.
7. (Science: chemical) a mass of earthy matter, or rock of the same character as the wall rock, occurring in the course of a vein, as of coal or ore; hence, to take horse said of a vein is to divide into branches for a distance.
8. See Footrope, a breastband for a leadsman.
An iron bar for a sheet traveler to slide upon.
a jackstay.
horse is much used adjectively and in composition to signify of, or having to do with, a horse or horses, like a horse, etc.; as, horse collar, horse dealer or horsedealer, horsehoe, horse jockey; and hence, often in the sense of strong, loud, coarse, etc.; as, horselaugh, horse nettle or horse-nettle, hors
c93
eplay, horse ant, etc. Black horse, blood horse, etc. See black, etc. Horse aloes, caballine aloes.
(Science: zoology) horse ant, a large ant (formica rufa); called also horse emmet. Horse artillery, that portion of the artillery in which the cannoneers are mounted, and which usually serves with the cavalry; flying artillery.
(Science: botany) horse balm, a plant of the genus Hippocrepis (H. Comosa), cultivated for the beauty of its flowers; called also horsehoe vetch, from the peculiar shape of its pods. Iron horse, a locomotive. Salt horse, the sailors name for salt beef. To look a gift horse in the mouth, to examine the mouth of a horse which has been received as a gift, in order to ascertain his age; hence, to accept favors in a critical and thankless spirit. To take horse. To set out on horseback. To be covered, as a mare. See definition 7 (above).
Origin: as. Hors; akin to os. Hros, D. & OHG. Ros, g. Ross, Icel. Hross; and perh. To L. Currere to run, E. Course, current cf. Walrus.
Dictionary > Horse
You will also like...

Biosecurity and Biocontrol
This lesson explores the impact of biosecurity threats, and why they need to be identified and managed. Examples to incl..

Geological Periods
Geological periods is a study guide that cites the different geological periods on Earth's timeline. Each has a brief ov..
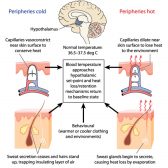
Temperature Regulation in Animals
This tutorial elucidates body temperature regulation. Know the details here to learn how the body sets the body temperat..
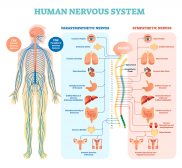
The Human Nervous System
The nervous system is essentially a biological information highway. This tutorial gives an overview of the nervous syste..

Mammalian Ancestors
Mammals are a diverse group of organisms, where most of them develop their offspring within the uterus of the mother. Ov..

Biological Cell Introduction
It only takes one biological cell to create an organism. A single cell is able to keep itself functional through its 'mi..

