Definition
noun
A membrane enzyme that allows the diffusion of protons (hydrogen ions) through its proton channel component while using the energy released from the proton gradient to produce ATP this time through its synthase domain.
Supplement
This enzyme is present in bacterial cell membrane, in inner mitochondrial membrane, and in thylakoid membrane in chloroplasts.
It consists of two major segments: Fo portion, the transmembrane proton channel and F1 portion, the synthase domain. The proton channel component allows the diffusion of protons (hydrogen ions) from an area where there are more hydrogen ions to an area where there are less hydrogen ions due to a proton gradient. As the proton (H+ ion) moves down the concentration gradient this moves the enzyme in a spinning motion, which brings ADP and inorganic phosphate together to form a bond, thus creating ATP molecule. The resulting ATP molecule is released so that a new ADP molecule can enter for another phosphorylation.
See also: chemiosmosis
Dictionary > Hydrogen-transporting ATP synthase
You will also like...

Fish
The sea was teeming with life. Eventually, through reproduction and continued variation, fish came about. There are over..
Primitive Animals
Life, as we know it today, is presumed to have started in the sea and many of them were likely eukaryotic animal-like or..
Human Reproduction and Fertilization
For human species to obviate extinction, reproductive mature adults should be producing viable offspring in order to con..
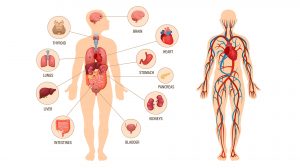
The Human Physiology
Physiology is the study of how living organisms function. Thus, human physiology deals specifically with the physiologic..
Control of Growth & Development
Control of Growth & Development tutorials look at how the genetic makeup determines the biological processes on a da..
Amphibians & Early Reptiles
Obtaining air outside an aquatic environment required species to acquire suitable adaptations, and this was the case of ..

