Ignition
(Science: radiobiology) in fusion, as in an ordinary (chemical) fire, ignition is the point where the temperature and confinement of heat in the fuel (plasma in the case of fusion) are such that energy released from ongoing reactions is sufficient to maintain the temperature of the system, and no external heating is needed. An ignited fusion plasma produces so much energy from fusion reactions that the plasma is fully heated by fusion reaction products (alpha particles in the case of D-T fusion), and the plasma no longer needs any external source of power to maintain its temperature. (The plasma may, however, still need something to maintain its confinement, this gives us control over the fusion reaction and helps prevent fusion reactors from having meltdown problems like fission reactors.)
Dictionary > Ignition
You will also like...

Consciousness and Behavior
Human consciousness and behavior are an interesting topic since they are determined and controlled by the brain. Conscio..
Plant Meristems and Growth
In plants, growth occurs in meristems, which are the site of repeated cell division of unspecialized cells. These cells ..
Birth Control and Contraception
Different pregnancy and birth control and contraception strategies are described. Read this tutorial to learn each of th..

Cell Respiration
Cell respiration is the process of creating ATP. It is "respiration" because it utilizes oxygen. Know the different stag..

Photosynthesis – Photolysis and Carbon Fixation
Photosynthesis is the process that plants undertake to create organic materials from carbon dioxide and water, with the ..
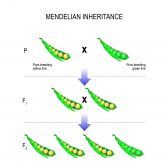
Inheritance and Probability
Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk, is most famous in this field for his study of the phenotype of pea plants, including ..

