Imitation
1. The act of imitating. Poesy is an art of imitation, . . . That is to say, a representing, counterfeiting, or figuring forth. (Sir P. Sidney)
2. That which is made or produced as a copy; that which is made to resemble something else, whether for laudable or for fraudulent purposes; likeness; resemblance. Both these arts are not only true imitations of nature, but of the best nature. (Dryden)
3. One of the principal means of securing unity and consistency in polyphonic composition; the repetition of essentially the same melodic theme, phrase, or motive, on different degrees of pitch, by one or more of the other parts of voises. Cf. Canon.
4. (Science: biology) The act of condition of imitating another species of animal, or a plant, or unanimate object. See imitate.
imitation is often used adjectively to characterise things which have a deceptive appearance, simulating the qualities of a superior article; opposed to real or genuine; as, imitation lace; imitation bronze; imitation modesty, etc.
Origin: L. Imitatio: cf. F. Imitation.
Dictionary > Imitation
You will also like...

Arthropods
The arthropods were assumed to be the first taxon of species to possess jointed limbs and exoskeleton, exhibit more adva..

Adaptation Tutorial
Adaptation, in biology and ecology, refers to the process or trait through which organisms or the populations in a habit..

Darwin and Natural Selection
This tutorial investigates the genetic diversity in more detail. It also delineates how certain alleles are favored over..

Photosynthesis – Photolysis and Carbon Fixation
Photosynthesis is the process that plants undertake to create organic materials from carbon dioxide and water, with the ..
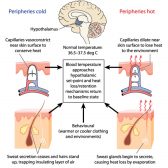
Temperature Regulation in Animals
This tutorial elucidates body temperature regulation. Know the details here to learn how the body sets the body temperat..

The Water Cycle
The water cycle (also referred to as the hydrological cycle) is a system of continuous transfer of water from the air, s..

