Influenza
An acute viral infection involving the respiratory tract, occurring in isolated cases, in epidemics or in pandemics striking many continents simultaneously or in sequence. It is marked by inflammation of the nasal mucosa, the pharynx and conjunctiva and by headache and severe, often generalised myalgia. Fever, chills and prostration are common. Involvement of the myocardium and of the central nervous system occur infrequently. A necrotising bronchitis and interstitial pneumonia are prominent features of severe influenza and account for the susceptibility of patients to secondary bacterial pneumonia due to streptococcus pneumoniae, haemophilus influenzae and staphylococcus aureus. The incubation period is one to three days and the disease ordinarily lasts for three to ten days. Influenza is caused by a number of serologically distinct strains of virus, designated a (with many subgroups), B and c.
Synonym: flu, grippe.
Dictionary > Influenza
You will also like...
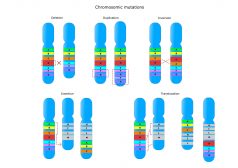
Chromosome Mutations
Mutations can also influence the phenotype of an organism. This tutorial looks at the effects of chromosomal mutations, ..

Plant Tissues
Plant organs are comprised of tissues working together for a common function. The different types of plant tissues are m..

Cell Biology
The cell is defined as the fundamental, functional unit of life. Some organisms are comprised of only one cell whereas o..

Examples of Natural Selection
Darwin's Finches are an example of natural selection in action. They are an excellent example of the way species' gene p..

Roots
This study guide tackles plant roots in greater detail. It delves into the development of plant roots, the root structur..

Genetic Engineering Advantages & Disadvantages
This tutorial presents the benefits and the possible adverse eventualities of genetic engineering. Know more about this ..

