Inorganic compound
n., plural: inorganic compounds
[ˌɪnɔːˈɡænɪk kŏm′pound′]
Definition: a compound without C-C or C-H bonds
Table of Contents
Inorganic Compound Definition
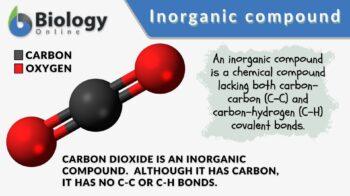
An inorganic compound is a chemical compound lacking both carbon-carbon (C-C) and carbon-hydrogen (C-H) covalent bonds. A chemical compound is made up of two or more elements that are chemically bonded together. One of the ways to classify compounds is by identifying them as either organic or inorganic.
Some would define an organic compound as a type of compound that contains a carbon atom. Conversely, an inorganic compound would be one that does not contain carbon.
However, not all carbon-containing compounds are organic. For example, carbon dioxide is an inorganic compound; although it has a carbon atom it has no C-C or C-H bonds.
Etymology: named after the early notion that inorganic compounds are not of biological origin
Compare: organic compound
Watch this vid about inorganic compounds:
Vitalism vs. Wöhler’s Findings
One of the predominant theories in the early centuries is vitalism. According to this theory, living things had a sort of a vital force –vis-vitalis – that made them distinct from non-living things. This vital force enabled them to produce certain chemicals that non-living things would not be able to produce.
The chemicals that living things produced had been called organic since they came from organisms. Those that were obtainable from non-living things had been called inorganic, meaning “not organic”. This was the fundamental boundary that defined organic from inorganic compounds.
Inorganic compounds were thought of as compounds that were not derived from organisms. They may be derived, for instance, from geological systems, e.g. sediments and ores.
This belief had long been held for many centuries until Friedrich Wöhler (1800 – 1882) disputed it with empirical evidence from his experiments. In one of his experiments, he found out that urea, which was once thought to be produced only by living things, could be produced from inorganic precursors. He discovered in 1828 that urea could be chemically produced from salts potassium cyanate and ammonium sulfate. This is considered a crucial turning point that later led to the rise of modern organic chemistry.
Confusions
At the height of vitalism, there had been a clear demarcation between organic and inorganic compounds. With the discrediting of vitalism, consensus on a modern definition for organic and inorganic compounds has not been reached among chemists. Merely saying that an organic compound is any compound that contains a carbon atom will not be absolutely correct as it will allude to the inclusion of some carbon-containing inorganic compounds.
The Inorganic Crystal Structure Database, a database of inorganic crystal structure data founded by Günter Bergerhoff and I.D.Brown in 1978, defined inorganic carbon compounds as compounds containing either C-H or C-C bonds. (Ref.1)
Carbon-containing compounds considered inorganic are the following: carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, carbides, thiocyanates, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide.
Allotropes of carbon, like a diamond, are not compounds but a pure element of carbon. Thus, they are not inorganic compounds but inorganic substances.
Organic vs. Inorganic Compounds
The generalized differences between organic and inorganic compounds are shown below:
Table 1: Organic Compounds vs. Inorganic Compounds | ||
|---|---|---|
| Organic Compounds | Inorganic Compounds | |
| Presence of carbon atoms | Mostly containing carbon atoms | Mostly lacking carbon atoms |
| Chemical bonding | Covalent bonding; mostly with carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bonds | Mostly ionic bonding; mostly lacking C-H bonds |
| Origin | Essentially, biological (as a result of biological activity) | Chemical (from laboratory works or experiments) or geological (as a result of a natural process unrelated to life) |
| Salt formation | Cannot form salt | Can form salt |
| Metal atoms | Do not contain metal atoms | May contain metal atoms |
| Other features | In most of the aqueous solutions, poor conductors of heat and electricity | Mostly, good conductors of heat and electricity |
| Examples | carbohydrates, fats, proteins, nucleic acids, urea, carbon tetrachloride | sodium chloride, brass, glass, carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, carbides, thiocyanates, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, water |
As pointed out earlier, there is no clear distinction between an organic and inorganic compound. Exceptions exist in every feature. Thus, the tabulated differences between the two should be taken as true for most cases but not all.
Types of Inorganic Compounds
A chemical compound is a substance consisting of atoms or ions of two or more elements that are chemically bonded together whereas a chemical element is a substance of only one type of atom. Most elements are inorganic but technically are not inorganic compounds since they are comprised of only one type of atom. Thus, the classification of inorganic compounds entails the grouping of substances comprised of more than one type of atom. Conversely, simple inorganic substances (not necessarily compounds) are typified as either metal or non-metal. However, there is no clear distinction between metals and non-metals.
Most inorganic compounds are ionic compounds. This means that the chemical bond that holds the atoms together is an ionic bond. Based on inorganic compound constituents, ionic compounds could be classified into bases, acids, and salts.
The ionic bond is the bond where there is a complete transfer of an electron from one atom to another. It is an electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, i.e. cation and anion. A cation is a positively charged ion whereas an anion is a negatively charged ion. For instance, sodium chloride is an ionic compound where the cation Na+ and the anion Cl– are held together by an ionic bond.
An ionic compound that has hydrogen ions (H+) is classified as an acid. Conversely, an ionic compound that has hydroxide (OH–) or oxide (O2-) is classified as a base. An ionic compound formed by acid-base reactions and without those ions is called a salt.
Water is definitely one of the most important inorganic compounds to all living things. It is a compound comprised of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. However, it is not an ionic compound but a molecule held by covalent bonding between hydrogen and oxygen.
Sciences
The study of the properties and synthesis of organic compounds is known as organic chemistry whereas the study of properties and synthesis of inorganic chemistry is called inorganic chemistry.
Take the Inorganic Compound Biology Quiz!
Reference
- Wayback Machine. (2017, January 1). Inorganic Crystal Structure Database: Scientific Manual. Retrieved from PDF
© Biology Online. Content provided and moderated by Biology Online Editors