Lamprey
(Science: zoology) An eel-like marsipobranch of the genus petromyzon, and allied genera. The lampreys have a round, sucking mouth, without jaws, but set with numerous minute teeth, and one to three larger teeth on the palate. There are seven small branchial openings on each side.
The common or sea lamprey of America and Europe (petromyzon marinus), which in spring ascends rivers to spawn, is considered excellent food by many, and is sold as a market fish in some localities. The smaller river lampreys mostly belong to the genus Ammocoeles, or Lampetra, as a. Fluviatilis, of Europe, and a. Aepypterus of America. All lampreys attach themselves to other fishes, as parasites, by means of the suckerlike mouth.
alternative forms: lamper eel, lamprel, and lampron.
Origin: oe. Lampreie, f. Lamproie, LL. Lampreda, lampetra, from L. Lambere to lick – petra rock, stone. The lampreys are so called because they attach themselves with their circular mouths to rocks and stones, whence they are also called rocksuckers. See lap to drink, Petrify.
Primitive eellike freshwater or anadromous cyclostome having round sucking mouth with a rasping tongue.Pertaining to species of animals who do not possess a jaw bone.
Dictionary > Lamprey
You will also like...

Still Freshwater & Plants
Plants in lentic habitats have features not found in terrestrial plants. They acquired these features as they adapt to t..

Soils
Nutrients in the soil are essential to the proper growth of a land plant. This tutorial deals with the properties of soi..
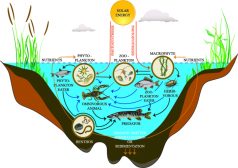
Freshwater Producers and Consumers
Freshwater ecosystem is comprised of four major constituents, namely elements and compounds, plants, consumers, and deco..
Birth Control and Contraception
Different pregnancy and birth control and contraception strategies are described. Read this tutorial to learn each of th..
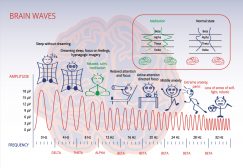
Sleep and Dreams – Neurology
While learning and intelligence are associated with the functions of a conscious mind, sleep and dreams are activities o..
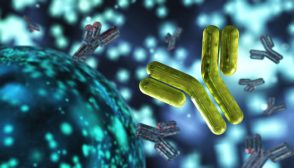
Passive and Active Types of Immunity
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell capable of producing a specific immune response to unique antigens. In thi..

