
Lanugo
n., plural: lanugos
[ləˈnjuːɡəʊ]
Definition: thin, soft, and poorly pigmented hair that covers the body of the fetus or a newborn
Table of Contents
What is Lanugo?
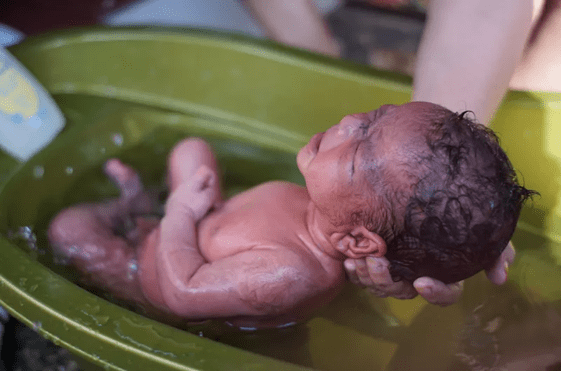
Lanugo is the delicate and downy hair that covers a fetus within the uterus (womb). It is very fine hair. It aids in their protection and keeps them warm as they grow. Some neonates, particularly those delivered pre-term, have lanugo on their bodies during birth.
It begins to appear around 16 weeks of gestation. It is believed to serve as an anchor to hold the vernix caseosa (i.e. a waxy, white coat) on the skin of the fetus. Lanugo is typically shed before birth, typically at about 33 to 36 weeks of gestation. However, it may persist even after birth; therefore, the newborn may be seen covered with lanugo.
When this happens, the lanugo is soon shed within a few weeks. Lanugo is replaced by another type of hair called vellus hair, which is thinner than the former.
Eating disorders and malignancies have also been found to cause lanugo.

Watch this vid about lanugo:
Biology definition:
Lanugo is the thin, soft, and poorly pigmented hair, and is the first to be produced by the hair follicle, particularly in the skin of a developing fetus. In humans and other mammals, lanugo is the type of hair that covers the body of the fetus or a newborn. It is the first type of hair produced by hair follicles.
Etymology: Latin lānūgō (down, wooliness), from lana (wool)
Synonyms: primary hair; downy hair
See also: vellus hair, terminal hair
Related form: lanuginous (adjective, covered with lanugo)
Mentioned in: hypertrichosis
Who Gets Lanugo?
Lanugo is more prevalent in prenatal infants and neonates. Nonetheless, individuals with eating problems or specific tumors or diseases can develop lanugo.
Fetal development
Unborn babies acquire lanugo during 16-20 weeks of gestation. The entire body is covered except for areas having unpigmented hair. Lips, palms, toenails, and soles of the feet are areas without hair follicles. Usually, lanugo is shed before delivery, however, some newborns still possess it.
Pre-mature babies often have lanugo. If you have a lanuginous baby, the lanugo should naturally vanish over time. It is common to have lanugo hair on the baby’s forehead or a newborn with a full head of hair. Hairs on the face or forehead usually vanish within two or three months.
People with anorexia or bulimia
Lanugo in adults and children might develop due to an eating disorder. They might also have lanugo on their face. Why do anorexics have lanugo? Experts believe this may occur because their body has problems sustaining heat. The development of lanugo anorexia nervosa is frightful.
Did you know…?
Anorexic or bulimic individuals may form lanugo on their bodies, including faces, which may indicate severe malnourishment.
Certain types of tumors
Teratoma sufferers can develop lanugo hair. Teratomas are rare germ cells that may be cancerous or noncancerous.
Function
What is the purpose of lanugo?
What does lanugo do? Fetal lanugo is important. It covers the baby’s delicate skin and keeps them warm in the womb. How about vernix, what is vernix? Vernix is the waxy, cheese-like substance that covers the fetus.
Lanugo assists vernix in adhering to the epidermis. Vernix on baby’s body from amniotic fluid in the pregnancy. Without lanugo and vernix, the amniotic fluid could harm their sensitive skin.
Vernix protects and insulates the body when held by lanugo. Lanugo keeps your baby warm until they gain enough body fat to do so.
Lanugo helps babies grow. Vibrating lanugo boosts the baby’s sensory receptors. These receptors help babies develop. When lanugo falls out, baby growth slows. Experts are still studying the hormonal effects of lanugo and the exact mechanism. (Anastassakis, 2022)
When does lanugo fall off?
When do babies lose their hair? The newborn loses hair shortly before birth. About 30 percent of full-term infants have hair. Lanugo is more prone to occur in infants delivered preterm (before 37 weeks). A few weeks may pass, and lanugo will finally shed on its own.
During the last eight weeks of pregnancy, lanugo typically comes off. It combines with amniotic fluid as soon as it is shed. As a result of ingesting amniotic fluid in the uterus, your infant’s first diet includes lanugo. In their first stool, known as meconium, newborns will expel the tiny hairs. (Grubbs, 2021)
When does a baby’s hair grow? After lanugo is removed, your infant will develop vellus hair, which resembles peach fuzz. Vellus hair regulates body temperature until the development of adult hair (terminal hair) begins to develop. All of these baby hairs have their own importance and should not be removed as it is a common practice in some cultures
Why do people with eating disorders get lanugo?
Adults with anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, or other eating disorders may develop lanugo. It can be a skin sign of poor nutrition and malnutrition. Professionals in the medical field believe lanugo develops when a person has no sufficient body fat to keep them warm. As a result, their bodies manufacture lanugo for insulating purposes. (Clinic 2022)
Anatomy
What does lanugo look like?
Lanugo is delicate, thin, and baby light hair. If your baby is born with lanugo hairs, he or she may appear to be covered in a coating of soft fur. Lanugo is not present in areas where there is no hair growth are the palms, nails, lips, genitalia, and soles of the feet. Lanugo is most visible on a baby’s back, shoulders, and tailbone, although it can appear anyplace there are hair follicles. Sometimes. It is present on the baby’s eyebrows.
What color is lanugo hair?
Lanugo hair color can range from very light to quite dark. A baby’s hair color may be light or dark depending on his or her genetic makeup. For instance, lanugo may be more noticeable on a darker complexion than on one with light skin babies.
What happens to a baby’s lanugo hair?
Why do babies lose their hair? In the seventh or eighth month of pregnancy, the unborn child’s lanugo hair begins to fall out. In this situation, the lanugo is eaten by the infant after combining with amniotic fluid. However, certain infants, particularly those born before 37 weeks gestation, are born with lanugo (premature). If your baby is born with lanugo hair, it will naturally fall out over time. (Clinic 2022)
Conditions and Disorders
When is growing lanugo a sign of a medical condition?
When observed on neonates, lanugo is not caused for concern. However, lanugo can be caused by severe eating disorders or starvation. Rarely, it has been associated with tumors or malignancy. If a woman has lanugo hairs or any other adult, you should consult a healthcare professional.
Is it bad for a baby to be born with lanugo?
No, having lanugo on a baby’s body is not a cause for concern at all. It is not abnormal to have lanugo new-born as hair on their skin if they were delivered prematurely. It is conceivable for a full-term baby to have lanugo at delivery, but the likelihood of this happening is minimal. After a few weeks, the lanugo should have shed completely.
How do you treat lanugo on an adult?
In adults, treating lanugo requires treating the ailment that is causing it. The first thing that needs to be done to treat anorexia, bulimia, or any other type of eating disorder is to receive professional assistance. In underweight people, lanugo grows as a protective strategy to help them keep their body temperature stable.
If your healthcare professional determines that lanugo is caused by a tumor, the tumor will almost always be removed. Even if the tumor is not malignant, it still has the potential to rupture or cause other complications. After the surgical removal of the tumor, the healthcare provider may recommend chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of the two treatments in addition to surgical removal. If the tumor is effectively treated, the lanugo hairs should cease to develop. (Clinic 2022)
Care
When will lanugo hair go away on newborns?
Within the first two months of a baby’s existence, the lanugo will fall out. On the other hand, some newborns retain very fine, soft downy hair that resembles peach fuzz on the tops of their ears, above their tailbones, and at the base of their necks. This is normal and you shouldn’t feel concerned about it in any way. Talk to your child’s pediatrician if you have any concerns or questions regarding the body hair that is growing in the infant.
Should you remove lanugo hair?
No, you should just not wax, shave, or get rid of your baby’s lanugo hair in any other way. The skin of your newborn baby is quite sensitive, and this will irritate it. Shaving or waxing can be a choice for you if you’re an adult with lanugo and you want to get rid of it. However, until the underlying issue is treated, it will continue to grow back.
Answer the quiz below to check what you have learned so far about lanugo.
References
- Anastassakis, K. (2022). Types of Hair Follicles in Humans. In Androgenetic Alopecia From A to Z (pp. 77-81). Springer, Cham.
- Clinic, C. (2022). “Lanugo “. Retrieved 08 Aug, 2022, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/22487-lanugo.
- Grubbs, H., Nassereddin, A., & Morrison, M. (2021). Embryology, Hair. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing.
©BiologyOnline.com. Content provided and moderated by Biology Online Editors.








