Lemon
1. (Science: botany) An oval or roundish fruit resembling the orange, and containing a pulp usually intensely acid. It is produced by a tropical tree of the genus Citrus,the common fruit known in commerce being that of the species c. Limonum or c. Medica (var. Limonum). There are many varieties of the fruit, some of which are sweet.
2. The tree which bears lemons; the lemon tree.
(Science: botany) lemon grass, a white crystalline substance, inappropriately named, as it consists of an acid potassium oxalate and contains no citric acid, which is the characteristic acid of lemon; called also salis of sorrel. It is used in removing ink stains. See oxalic acid, under oxalic.
Origin: f. Limon, Per. Limn; cf. Ar.laimn, sp. Limon, It. Limone. Cf. Lime a fruit.
Dictionary > Lemon
You will also like...

Soils
Nutrients in the soil are essential to the proper growth of a land plant. This tutorial deals with the properties of soi..

Pollution in Freshwater Ecosystems
There are many environmental factors that arise due to the usage of water in one way or another and for every action tha..

Cell Biology
The cell is defined as the fundamental, functional unit of life. Some organisms are comprised of only one cell whereas o..

Meiosis and Alternation of Generations
Plants are characterized by having alternation of generations in their life cycles. This tutorial is a review of plant m..

Still Freshwater & Plants
Plants in lentic habitats have features not found in terrestrial plants. They acquired these features as they adapt to t..
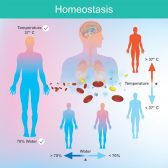
Physiological Homeostasis
Homeostasis is essential to maintain conditions within the tolerable limits. Otherwise, the body will fail to function p..

