Mac
a serious opportunistic infection caused by two similar bacteria (mycobacterium avium and mycobacterium intercellulare) found in the soil and dust particles. In aids, mac can spread through the bloodstream to infect lymph nodes, bone marrow, liver, spleen, spinal fluid, lungs and intestinal tract. Typical symptoms of mac include night sweats, weight loss, fever, fatigue, diarrhoea and enlarged spleen. Mac is usually found in people with cd4 counts below 100. Mac is also called mai.
Dictionary > Mac
You will also like...

Regulation of Biological Systems
Regulation of Biological Systems tutorials are focused on the modulation of biological systems from cell to population l..

Neural Control Mechanisms
Neurons generate electric signals that they pass along to the other neurons or target tissues. In this tutorial, you wil..

Evolution of Life – Ancient Earth
Autotrophs flourished, absorbing carbon and light. Soon after, primitive life forms that could assimilate oxygen thrived..
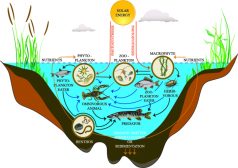
Freshwater Producers and Consumers
Freshwater ecosystem is comprised of four major constituents, namely elements and compounds, plants, consumers, and deco..

Population Regulation in an Ecosystem
With regard to the population size of a species and what factors may affect them, two factors have been defined. They ar..

Still Water Animals
Animals living in aquatic habitats have diversified and evolved through time. They eventually occupy ecological niches a..

