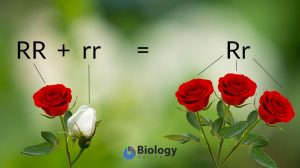Definition
noun
(genetics) A type of biological inheritance that conforms to the set of principles of Gregor Mendel regarding the transmission of genetic characters from parent organisms to their offspring through his scientific and cautious breeding experiments on pea plants
Supplement
Mendelian inheritance is a set of principles according to the generalizations of Gregor Mendel. Mendel proposed principles regarding the transmission of genetic characters from parent organisms to their offspring based on his scientific and cautious breeding experiments on pea plants. His findings were presented and published in a two-part paper, Experiments on Plant Hybridization in 1860s. His significant contributions were the cornerstone of genetics.
Gregor Mendel is an Augustinian monk and botanist who formulated the laws of heredity based on his experiments on garden pea plant breeding. Later, he was recognized for his seminal works on genetics. For this, he is recognized as the Father of Genetics. Breeding and testing about 5,000 pea plants, he was able to come up with essential generalizations that were used as founding principles of Mendelian inheritance or Mendel’s Principles of Heredity. He presented the so-called “Mendel’s laws of inheritance”, particularly the Law of Segregation, the Law of Independent Assortment, and the Law of Dominance”.
Compare:
See also: