Microparasites
(Science: epidemiology) Typically, viruses, bacteria, fungi and protozoa. More generally, parasites that multiply within their definitive hosts. Microparasites are characterized by small size, short generation times, and a tendency to induce immunity to re-infection in those hosts that survive. The duration of infection is usually short in relation to the lifespan of the host, but there are important exceptions, such as the slow viruses. The key epidemiological variable, by contrast with macroparasites, is whether or not the individual host is infected.
Dictionary > Microparasites
You will also like...
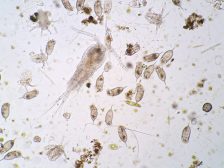
Freshwater Communities & Plankton
Planktons are microscopic organisms that live suspended in aquatic habitats. There are two groups: the phytoplanktons an..
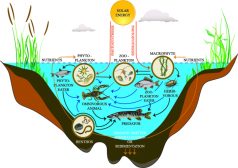
Freshwater Producers and Consumers
Freshwater ecosystem is comprised of four major constituents, namely elements and compounds, plants, consumers, and deco..

Plant Water Regulation
Plants need to regulate water in order to stay upright and structurally stable. Find out the different evolutionary adap..

A Balanced Vitamin Diet – Vitamins A – K
A balanced diet is essential to a healthy organism. Insufficiency or too much of a particular element or compound, such ..

Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Proteins have a crucial role in various biological activities. Get to know how proteins are able to perform as enzymes, ..

Abiotic and Biotic Factors
This tutorial deals with the abiotic factors of the freshwater environment that determine what sort of life would be sui..

