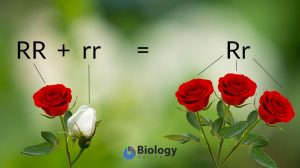Definition
noun, plural: monogenes
(genetics) Single gene controlling the expression of a particular trait
Supplement
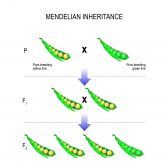
In genetics, the term monogene refers to the single gene involved in the expression of a trait. This is in contrast to the polygene, which is a group of genes producing a specific phenotype or trait only when expressed together. The related form monogenic is a descriptive word that relates to a single gene or allele. Terms that are derived from this word are monogenic inheritance and monogenic disorder. In particular, monogenic inheritance is a form of inheritance where a dominant allele influences the complete trait. It is in contrast to the polygenic inheritance where multiple genes are expressed for a particular trait. A monogenic disease is an inherited disease determined by the interaction of a single pair of genes. This is in contrast to a polygenic condition wherein several genes (polygene) are involved. In humans, the monogenic disease is less frequent than the polygenic disease. It is also less complicated than the latter and may follow a pattern based on Mendelian inheritance. Since monogenic disease involves a single pair of genes the dysfunctional or mutated gene may be identified more easily than polygenic disease.
Word origin: monos (one) + gene
See also:
Related form(s):