Multipolar mitosis
Abberant mitotic figures, where the chromosomal material is pulled to more than two poles. Multipolarity is usually a phenomenon associated with the increase in centrosome number. The fate of multipolar spindles is still under discovery, but it appears that various outcomes are possible. First, the poles may coalesce back together and the cell might divide in a bipolar fashion producing two daughter cells. Second, the cell might give rise to more than two cells not necessarily equal to the number of poles observed during metaphase. Third, the cell might arrest without ever completing cytokinesis. In cases where cell division takes place following multipolar mitosis, it is almost impossible for cells to aquire proper distribution of chromosomes, hence multipolarity is considered a major source of genomic instability.
Dictionary > Multipolar mitosis
You will also like...

Respiration
The human respiratory system is an efficient system of inspiring and expiring respiratory gases. This tutorial provides ..

Sugar Homeostasis
The blood sugar level is regulated by two hormones. The mechanism behind this type of negative feedback control is descr..

Principles of Hormonal Control Systems
Hormones are essential in the regulation of the activity of the various biological systems of the human body. The ineffi..
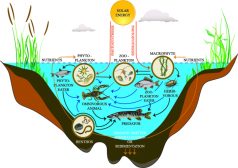
Freshwater Producers and Consumers
Freshwater ecosystem is comprised of four major constituents, namely elements and compounds, plants, consumers, and deco..

The Dinosaurs
Dinosaurs represented a major turn in the evolutionary development of organisms on Earth. The first dinosaurs were presu..

Animal Growth Hormones
Hormones are produced in the endocrine glands of animals. The pituitary gland and hypothalamus are the most impor..

