Definition
noun
A passive immunity acquired by the fetus or newborn from the mother via the placental transfer of antibodies during pregnancy and via breast milk. This type of immunity is short-lived, lasting the first six months of the newborn’s life.
Supplement
Adaptive immunity is divided into two types: natural immunity and artificial immunity. Natural immunity is further divided into natural passive immunity and natural active immunity. Artificial immunity can also be divided into artificial passive immunity and artificial active immunity.
Passive immunity is typically short lived (compared to active immunity). Passive immunity may be naturally acquired or artificially acquired. Maternal passive immunity is one type of naturally acquired passive immunity wherein the maternal antibodies are passed through the placenta to the fetus during the third month of gestation. Another means is by passing the antibodies in the breast milk when breastfeeding.
Compare: natural active immunity, artificial passive immunity
See also: passive immunity
Dictionary > Natural passive immunity
You will also like...
Plant Meristems and Growth
In plants, growth occurs in meristems, which are the site of repeated cell division of unspecialized cells. These cells ..

Freshwater Lentic Communities & Animals
This tutorial looks at some of the communities in freshwater lentic habitats. For instance, symbiosis occurs in a commun..

Population Growth and Survivorship
This lesson looks at population attributes, regulation, and growth. It also covers population genetics, particularly gen..

Mātauranga Māori and Science
Mātauranga Māori is the living knowledge system of the indigenous people of New Zealand, including the relationships t..

Roots
This study guide tackles plant roots in greater detail. It delves into the development of plant roots, the root structur..
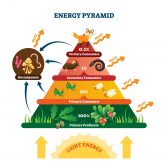
Freshwater Community Energy Relationships – Producers & Consumers
This tutorial looks at the relationship between organisms. It also explores how energy is passed on in the food chain an..

