Definition
noun, plural: neurons
An excitable cell that has specialized cell parts (such as soma, dendrites and axons), structures (such as synapses), and chemicals (such as neurotransmitters) for conducting nerve impulses
Supplement
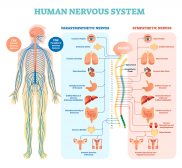
Neurons are nerve impulse-conducting cells that make up nerves, brain and spinal column. Thus, they are regarded as the functional unit of the nervous system. A typical neuron has a nucleated soma and processes (axon and dendrites).
Neurons may be classified according to polarity:
- bipolar neuron – a neuron in which the processes extend from opposite ends of the soma
- (pseudo)unipolar neuron – a neuron in which the process extends from one end of the soma
- multipolar neuron – a neuron in which an axon and several dendrites extend from the soma
Neurons according to the direction of nerve impulses:
- sensory (or afferent) neuron – a neuron sending nerve impulses toward the CNS
- motor (or efferent) neuron – a neuron sending nerve impulses away from the CNS to muscles or glands
- interneuron – a neuron sending impulses to another neuron
Word origin: Greek neûron (sinew, cord, nerve)
Variant(s):
- neurone (British)
Synonym(s):
- nerve cell
Related term(s):
- Mauthner neuron
- Golgi neuron
- Relay neuron
- Nanc neuron
- Nonadrenergic noncholinergic neuron
- Intercalary neuron
- Non-myelinated neuron
- Unmyelinated neuron
- Myelinated neuron
- Multipolar neuron
- Magnocellular neuron