Definition
noun
An anaerobe that does not require oxygen and lives only in anaerobic environment.
Supplement
Exposure to atmospheric levels of oxygen is lethal to obligate anaerobes. It is because they lack the enzymes like superoxide dismutase and catalase that would convert the lethal superoxide formed in their cells due to the presence of oxygen.
Obligate anaerobes may use fermentation or anaerobic respiration. Instead of oxygen, they use sulfate, nitrate, iron, manganese, mercury, or carbon monoxide as electron acceptors for respiration. The energy yield is lower than that in aerobic respiration.
Examples of obligate anaerobes are Bacteroides and Clostridium species.
Word origin: obligate » Latin obligātus (ptp. of obligāre), to bind + anaerobe » an- from Gk., “not, without,” + Greek āero-, from āēr, air.
Compare: obligate aerobe.
Dictionary > Obligate anaerobe
You will also like...

Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
Learn about the general structure of a eukaryotic gene, the transcription factors, and post-transcriptional regulation....

Cell Biology
The cell is defined as the fundamental, functional unit of life. Some organisms are comprised of only one cell whereas o..
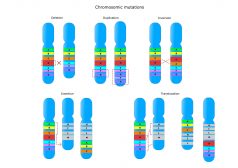
Chromosome Mutations
Mutations can also influence the phenotype of an organism. This tutorial looks at the effects of chromosomal mutations, ..

Water in Plants
The movement of molecules (specifically, water and solutes) is vital to the understanding of plant processes. This tuto..

New Zealand’s Biodiversity
Find out more about New Zealand's unique biodiversity by exploring a range of different ecosystems and the key role of s..
Homeostasis of Organism Water Regulation
Osmoregulation is the regulation of water concentrations in the bloodstream, effectively controlling the amount of water..

