Science (genetics, molecular biology, genomics) genes or gene products that are homologous (descended from a common ancestor) and are found in separate species due only to the speciation event (not to gene duplication). For example human hemoglobin alpha is orthologous to horse hemoglobin alpha, but is paralogous to both human and horse hemoglobin beta.
Compare: homology, paralogy
Dictionary > Orthology
You will also like...

Consciousness and Behavior
Human consciousness and behavior are an interesting topic since they are determined and controlled by the brain. Conscio..
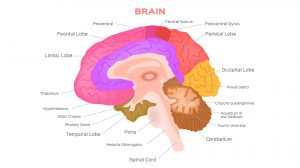
Human Neurology
Human Neurology deals essentially with the nervous system of humans. It also features the various theories put forward b..
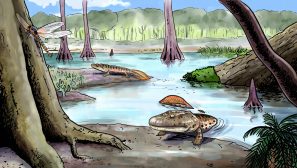
Amphibians & Early Reptiles
Obtaining air outside an aquatic environment required species to acquire suitable adaptations, and this was the case of ..

New Zealand’s Unique Flora
If New Zealand has lots of unique animals, it's also got a whole lot of unique plants. Find out more about some of them,..

Fruits, Flowers, and Seeds
This tutorial deals with the structure and function of flowers, fruits, and seeds. Also included here are the types of f..
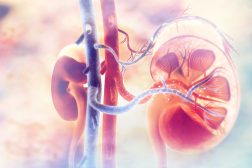
Homeostasis of Organism Water Regulation
Osmoregulation is the regulation of water concentrations in the bloodstream, effectively controlling the amount of water..

