Definition
noun
The part of the nervous system that relays between the central nervous system and the rest of the body, and is comprised of the autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system
Supplement
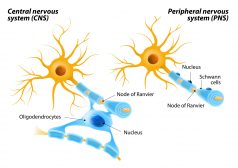
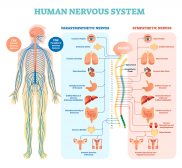
In vertebrates, the nervous system has two major divisions: (1) the central nervous system and (2) the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system consists of the brain, the brainstem, and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes the cranial nerves, the spinal nerves, the sympathetic nervous system, and the parasympathetic nervous system.
The peripheral nervous system is the part of the vertebrate nervous system that lies outside the central nervous system. It connects the central nervous system with the sensory organs, other organs, muscles, blood vessels, and glands. It is comprised of the cranial nerves, the spinal nerves, the sympathetic nervous system, and the parasympathetic nervous system. The peripheral nervous system is not protected by a bony structure, such as the brain by the skull and the spinal cord by the vertebral column of the central nervous system. Thus, the peripheral nervous system is more prone to mechanical or chemical injuries.
There are two main parts of the peripheral nervous system: the autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system is associated with involuntary muscle movements whereas the somatic nervous system is associated with voluntary muscle movements. The somatic nervous system has two main types of nerves: afferent nerves and efferent nerves.
Abbreviation / Acronym:
- PNS
Also called:
- systema nervosum periphericum
See also:
- cranial nerve
- neuron
- parasympathetic nervous system
- sympathetic nervous system
- nervous system
- somatic nervous system
- autonomic nervous system