physicology –>
physics
The science of nature, or of natural objects; that branch of science which treats of the laws and properties of matter, and the forces acting upon it; especially, that department of natural science which treats of the causes (as gravitation, heat, light, magnetism, electricity, etc) that modify the general properties of bodies; natural philosophy.
chemistry, though a branch of general physics, is commonly treated as a science by itself, and the application of physical principles which it involves constitute a branch called chemical physics, which treats more especially of those physical properties of matter which are used by chemists in defining and distinguishing substances.
See: physic.
Dictionary > Physicology
You will also like...

Population Growth and Survivorship
This lesson looks at population attributes, regulation, and growth. It also covers population genetics, particularly gen..
Meiosis – The Genetics of Reproduction
Meiosis is a form of cell division that creates gametes. It is comprised of two divisions that in the end, the resulting..
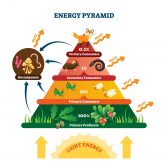
Freshwater Community Energy Relationships – Producers & Consumers
This tutorial looks at the relationship between organisms. It also explores how energy is passed on in the food chain an..

Stems
Stems primarily provide plants structural support. This tutorial includes lectures on the external form of a woody twig ..

Neural Control Mechanisms
Neurons generate electric signals that they pass along to the other neurons or target tissues. In this tutorial, you wil..

Fish
The sea was teeming with life. Eventually, through reproduction and continued variation, fish came about. There are over..

