Definition
noun, plural: ploidies
The number of sets of homologous chromosomes that make up the genome of a cell or an organism
Supplement
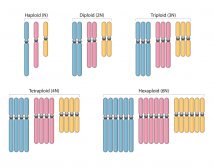
Ploidy refers to the number of sets of homologous chromosomes in the genome of a cell or an organism. Each set is designated by n. Accordingly, one set of chromosomes, 1n, is described as monoploid. However, the term haploid is used to describe gametes that contain only half of the set of the usual sets of chromosomes of the somatic cells of an organism. The union of two haploid gametes, i.e. female and male gametes, gives rise to a zygote with two sets of chromosomes thereby preserving the original chromosome number as that of the parents. The two sets of chromosomes would be homologous chromosomes, i.e. the chromosomes from the female gamete would have the corresponding chromosomes from the male gamete based on the likeness of morphology and linear sequence of gene loci. The cell or the organism with two sets of homologous chromosomes, 2n, is described as diploid. Having multiple sets of paired chromosomes in a genome of an organism is described as polyploid. Three sets of chromosomes, 3n, is triploid whereas four sets of chromosomes, 4n, is tetraploid. Extremely large number of sets may be designated by number (for example 15-ploid for fifteen sets).
See also:
Dictionary > Ploidy