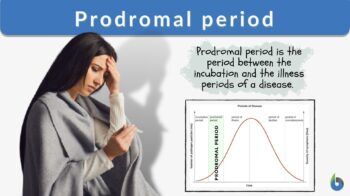
Prodromal period
n., [pɹəʊˈdɹəʊməl ˈpɪərɪəd]
Definition: Stage of a disease wherein the early signs and symptoms appear but not yet clinically specific nor severe
Table of Contents
There are five stages (or phases) of a disease. (Hattis, 2020). These stages are (1) Incubation period, (2) Prodromal period, (3) Illness period, (4) Decline period, and (5) Convalescence period.

Prodromal Period Definition
The prodromal period is also known as the prodromal stage. In this stage of the disease, there is an increase in the number of infections causing the immune system of the body to start to react against infectious agents. We can also define the prodromal period as a phase where the number of pathogens continues to increase. Before the specific symptoms of the disease appear, some early symptoms start appearing in this phase.
The prodromal period is the period characterized by the presence of early signs and nonspecific symptoms of a disease. It is the period between the incubation period and the illness period. During this period, the symptoms are not highly specific and the affected individual may feel discomfort but, generally, may still be able to perform usual functions.
Synonym: prodromal stage. See also: incubation period, illness period, convalescent period
What is prodrome?
In the field of medicine, the term “prodrome” is characterized as a stage in which some early signs and symptoms start to appear before the appearance of any specific diagnostic-related symptoms. These early signs and symptoms indicate the beginning of any disease.
“Prodrome” comes from the Greek word “prodromos”, which means “running before”. Sometimes, in the prodrome phase, the symptoms are non-specific, but sometimes they may relate to a particular disease.
For Example: In many infectious diseases, some symptoms that are non-specific and appear in the prodromal phase are loss of appetite, headache, malaise, and fever. (Kenneth W. Lindsay, 2011)
What happens in the prodromal phase?
After the incubation period, the prodromal period follows. In this period, the host had some symptoms like inflammation, pain, swelling, soreness, and fever. These general symptoms are due to the activation of the immune system. It is difficult to make a diagnosis based on these general signs and symptoms. The symptoms appear to be more exact and specific in the illness phase, which comes after the prodromal phase (Bhandari, 2020).
What is the prodromal period of an infectious disease?
In the prodromal period, the pathogens replicate continuously. The immune system of the body gets activated and some general symptoms start appearing. Symptoms are fatigue and low-grade fever. In the prodromal stage, there are higher chances that the host might transfer the infection to others.
It depends on the type of infection and how long the prodromal period lasts. For instance, the incubation period of flu is about 2 days. In this case, the prodromal period might overlap the incubation period and the beginning of the illness. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says that there are higher chances that the pathogen virus transfers to another one day earlier to the appearance of symptoms and up to the week after the illness period (Eske, 2021).
Watch this video below to understand the different stages of the disease.
Prodromal Phase of Common Diseases and Conditions
Some of the well-known prodromal symptoms of common diseases are described below.
- Prodromal phase of pneumonia
- Prodromal phase of malaria
- Prodromal phase of influenza
- Prodromal phase of meningitis
- Prodromal phase of schizophrenia
Prodromal phase of pneumonia
The prodromal signs of pneumonia in the patient include coughing (with bloody, green, or yellow mucus). The patient also had a lack of appetite, stabbing pain in the chest, shallow breathing, shortness of breath, low energy, chills, and fever.
- In bacterial pneumonia, the patient may have a high-grade fever. Due to insufficient oxygen in the blood, the patients may have blue nail beds.
- Viral pneumonia takes some days to develop but shows symptoms similar to influenza. The symptoms are dry cough, weakness, fever, muscular pain, and headache. A patient should get proper medical treatment if the symptoms (blue lips, fever) get worse in a few days.
Prodromal phase of malaria
In the prodromal phase of malaria, the symptoms are fever (remains for up to two days), lack of appetite, pain in the body, headache, and fatigue. If the patient has weak immunity, malaria starts with a sudden and extreme feeling of sickness. The fever may be at 39°C and higher. The fever does not follow a regular pattern. Some other symptoms include respiratory distress, confusion, vomiting, nausea, icterus, and dry cough.
Prodromal phase of influenza
The most common source of morbidity and mortality is influenza. Influenza is a worldwide occurring viral infection. This viral disease mainly spreads in two ways.
- Direct contact with the nasal secretion of patient
- Inhaling the coughed and sneezed droplets of the patients
The symptoms of the prodromal phase of infection include a runny and stuffy nose, sore throat, rigors, myalgia, malaise, and fever.
Prodromal phase of meningitis
The infection of protective membranes (meninges) that surrounds the brain and spinal cord is known as meningitis. It affects any person but most commonly it affects babies, teenagers, young children, and young adults. It proves a very serious condition if not treated timely. Some non-specific symptoms appear in the prodromal stage that may last throughout the illness. The symptoms are loss of appetite, respiratory disorder, headache, joint and muscular pain, irritability, lethargy, vomiting, nausea, and fever.
Some specific symptoms in the case of bacterial meningitis are seizures, stiffness in the neck, photophobia, headache, confusion, drowsiness, and focal neuro deficit.
Prodromal Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is defined as a chronic illness of the nervous system. It affects the way a person behaves, thinks, or feels. The thought of investigating the prodromal of schizophrenia is almost 100 years back but now it is recently accepted. There is an unusual behavioral alteration in this disease. The prodromal period of schizophrenia usually remains for several years. It causes many social consequences on the person. In the prodromal period, there are several cognitive and behavioral modifications in a person. Such modification continues to progress with time and leads to psychosis. Some symptoms of the prodromal period of schizophrenia are the problem in sleeping, anxiety, irritability, changes in daily routine, difficulty in concentration, neglecting personal hygiene, lack of motivation, erratic behavior, and social isolation (Subotnik, 1988).
Prodromal phase of schizophrenia
The prodromal phase of schizophrenia usually starts in the 20s or in the teenage years. Due to this, it is difficult that either the alteration in the behavior is due to schizophrenia or because of young adult behavior. Research for the treatment of schizophrenia includes those patients which are in their phase. Some researchers suggest that using some strategies and modifying them according to the need of the patient, may prove helpful for the patient in coping and give better results.
Try to answer the quiz below to check what you have learned so far about prodromal period.
References
- Bhandari, S. (2020). WebMD. From WebMD: https://www.webmd.com/schizophrenia/schizophrenia-prodrome
- Characteristics of Infectious Disease. (2021). LumenLearning. From: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/microbiology/chapter/characteristics-of-infectious-disease/
- Eske, J. (2021, March 3). Medical New TODAY. From Medical New TODAY: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/5-stages-of-infection#prodromal
- Hattis, R. (2020, March). The Five Stages of Disease and Prevention. From Research Gate: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279589860_The_Five_Stages_of_Disease_and_Prevention
- Kenneth W. Lindsay, I. B. (2011). Neurology and Neurosurgery Illustrated. UK.
- Subotnik, K. L. (1988). Prodromal signs and symptoms of schizophrenic relapse. Journal of
- Abnormal Psychology, 405–412.
©BiologyOnline.com. Content provided and moderated by Biology Online Editors.