Definition
noun
(1) A temporary deviation from a normal state in the opposite direction following an abrupt removal or discontinuation of a variable, such as a treatment suddenly discontinued after a long-term use, a passive resistance released suddenly, an undershoot, etc., in an effort to restore balance or homeostasis
(2) A condition wherein the maximum therapeutic effect is reached, and the opposite effect ensues
Supplement
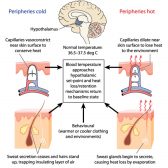
For example, a rebound phenomenon occurs when the sudden discontinuation of medication results in the relapse of symptoms that are worse than those before the treatment. Thus, treatments capable of causing rebound effects have to be withdrawn gradually. Another example is the posthypoglycemic hyperglycemia characterized by a rebound hyperglycemia after a period of hypoglycemia. When the blood glucose level is low the body tends to compensate by producing regulatory hormones that incite the liver to produce glucose from stored glycogen. Thus, the outcome is an increase of blood glucose or hyperglycemia. Another is the Stewart-Holmes sign seen in individuals with cerebellar deficit or a lesion in the cerebellum.
Rebound phenomenon is also described when rebound effects ensues after the individual developed tolerance to the drug. An example is the prolonged use of pain killers that lead to the development of tolerance to these drugs. Eventually, the pain killers become less effective. This leads to headaches that are more frequent or worse than before.
Word origin: French rebondir + Greek phainomenon anything seen
Also called:
- rebound effect
See also: